Korean red ginseng suppresses mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy
- PMID: 38223821
- PMCID: PMC10785417
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.07.002
Korean red ginseng suppresses mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy
Abstract
Background: Skeletal muscle denervation leads to motor neuron degeneration, which in turn reduces muscle fiber volumes. Recent studies have revealed that apoptosis plays a role in regulating denervation-associated pathologic muscle wasting. Korean red ginseng (KRG) has various biological activities and is currently widely consumed as a medicinal product worldwide. Among them, ginseng has protective effects against muscle atrophy in in vivo and in vitro. However, the effects of KRG on denervation-induced muscle damage have not been fully elucidated.
Methods: We induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice by dissecting the sciatic nerves, administered KRG, and then analyzed the muscles. KRG was administered to the mice once daily for 3 weeks at 100 and 400 mg/kg/day doses after operation.
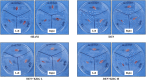
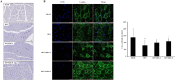
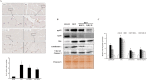
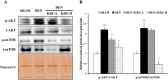
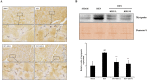
Results: KRG treatment significantly increased skeletal muscle weight and tibialis anterior (TA) muscle fiber volume in injured areas and reduced histological alterations in TA muscle. In addition, KRG treatment reduced denervation-induced apoptotic changes in TA muscle. KRG attenuated p53/Bax/cytochrome c/Caspase 3 signaling induced by nerve injury in a dose-dependent manner. Also, KRG decreases protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway, reducing restorative myogenesis.
Conclusion: Thus, KRG has potential protective role against denervation-induced muscle atrophy. The effect of KRG treatment was accompanied by reduced levels of mitochondria-associated apoptosis.
Keywords: Korean red ginseng; denervation; mitochondria-activated apoptosis; myogenesis.
© 2023 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no known competing conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Korean Red Ginseng suppresses emphysematous lesions induced by cigarette smoke condensate through inhibition of macrophage-driven apoptosis pathways.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Mar;48(2):181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.11.001. Epub 2023 Nov 7. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 38465217 Free PMC article.
-
Korean red ginseng decreases 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced mitophagy in SH-SY5Y cells.J Integr Med. 2021 Nov;19(6):537-544. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.09.005. Epub 2021 Sep 14. J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 34580047
-
Daily heat stress treatment rescues denervation-activated mitochondrial clearance and atrophy in skeletal muscle.J Physiol. 2015 Jun 15;593(12):2707-20. doi: 10.1113/JP270093. Epub 2015 May 20. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25900738 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on metabolic syndrome.J Ginseng Res. 2021 May;45(3):380-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34025131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginseng, the natural effectual antiviral: Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against viral infection.J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):309-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chestnut (Castanea crenata) Inner-Shell Extract Attenuates Barium-Chloride-Induced Injury and Denervation-Induced Atrophy in Skeletal Muscle of Mice.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 26;17(13):2116. doi: 10.3390/nu17132116. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647221 Free PMC article.
-
Pycnogenol-Assisted Alleviation of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Induced Lung Inflammation via Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein Downregulation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 9;13(8):972. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080972. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eisenberg H.A., Hood D.A. Blood flow, mitochondria, and performance in skeletal muscle after denervation and reinnervation. J Appl Physiol. 1994;76(2):859–866. 1985. - PubMed
-
- Wicks K.L., Hood D.A. Mitochondrial adaptations in denervated muscle: relationship to muscle performance. Am J Physiol. 1991;260(4 Pt 1):C841–C850. - PubMed
-
- Jackman R.W., Kandarian S.C. The molecular basis of skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;287(4):C834–C843. - PubMed
-
- Primeau A.J., Adhihetty P.J., Hood D.A. Apoptosis in heart and skeletal muscle. Can J Appl Physiol. 2002;27(4):349–395. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

