Niosomal Doxycycline and Triamcinolone: A Novel Approach to Minimize Cytotoxicity in Endodontic Medicaments
- PMID: 38223837
- PMCID: PMC10787185
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v19i1.42608
Niosomal Doxycycline and Triamcinolone: A Novel Approach to Minimize Cytotoxicity in Endodontic Medicaments
Abstract
Introduction: Mechanical root canal preparations and irrigation solutions are essential for reducing microbial counts in the root canal system. However, these methods do not completely eliminate microorganisms. Intracanal medicaments are used to further decrease microbial counts. This study aims to assess the cytotoxicity of various intracanal medicaments.
Materials and methods: In this in vitro study, murine fibroblast cell lines (L929) were cultured in a controlled environment. The MTT assay was employed to evaluate the cytotoxicity of different medicament combinations, including calcium hydroxide and triamcinolone (D1), niosomal doxycycline and triamcinolone (D2), calcium hydroxide (D3), and a combination of doxycycline and triamcinolone (D4). Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Dunnett's test.
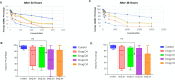
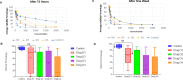
Results: The results indicated that D1 and D2 had lower cytotoxicity, while D4 exhibited the highest cytotoxicity. D1 was found to be non-cytotoxic up to a concentration of 500 µg/mL over a period of 72 hours. D2 and D3 showed similar effects up to concentrations of 250 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL, respectively, for 72 hours. In contrast, D4 exhibited cytotoxicity at concentrations above 75 µg/mL at 72 hours.
Conclusion: This study suggests that encapsulating doxycycline in niosomal structures (D2) reduces cytotoxicity in murine fibroblast cell lines (L929) for at least 24 and 48 hours. These findings offer promising implications for the development of endodontic medicaments with improved biocompatibility.
Keywords: Calcium Hydroxide; Corticosteroid; Cytotoxicity; Niosomal Doxycycline.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Evaluation of Nano Inorganic Metal Oxides as Intracanal Medicaments for Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activity in the Root Canal System.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023 Sep;16(Suppl 2):168-175. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2635. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023. PMID: 38078022 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Different Intracanal Medicaments on the Viability and Survival of Dental Pulp Stem Cells.J Pers Med. 2022 Apr 4;12(4):575. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040575. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35455691 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of calcium hydroxide nanoparticles on murine fibroblast cell line.Iran Endod J. 2015 Winter;10(1):49-54. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Iran Endod J. 2015. PMID: 25598810 Free PMC article.
-
Root canal medicaments.Int Dent J. 2009 Feb;59(1):5-11. Int Dent J. 2009. PMID: 19323305 Review.
-
Additive and reducing Effects between Calcium Hydroxide and Current Irrigation Solutions.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2017 Mar 1;18(3):246-249. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2017. PMID: 28258273 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the effectiveness of doxycycline in restorative dentistry: a systematic review of in vitro studies.Odontology. 2025 Jan;113(1):15-41. doi: 10.1007/s10266-024-00986-2. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 39133374
References
-
- Hübscher W, Barbakow F, Peters OA. Root‐canal Preparation with Flexmaster: Canal Shapes Analysed by Micro‐Computed Tomography. Int Endod J. 2003;36(11):740–7. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy J, Hussey D. The Antimicrobial Effects of Root Canal Irrigation and Medication. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103(4):560–9. - PubMed
-
- Awawdeh L, AL‐Beitawi M, Hammad M. Effectiveness of Propolis and Calcium Hydroxide as a Short‐Term Intracanal Medicament Against Enterococcus Faecalis: A Laboratory Study. Aust Endod J. 2009;35(2):52–8. - PubMed
-
- Peters OA, Peters CI, Schönenberger K, Barbakow F. ProTaper Rotary Root Canal Preparation: Assessment of Torque and Force in Relation to Canal Anatomy. Int Endod J. 2003;36(2):93–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources