Comparative Analysis of Photosensitizer Penetration Depth in Root Canal Debridement for Endodontic Disinfection
- PMID: 38223841
- PMCID: PMC10787188
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v19i1.41545
Comparative Analysis of Photosensitizer Penetration Depth in Root Canal Debridement for Endodontic Disinfection
Abstract
Introduction: Microbial agents play a crucial role in periapical lesions and despite mechanical preparation, presence of persistent bacteria in root canal system is a challenge. Photodynamic therapy offers a debridement method, utilizing photosensitizers such as Curcumin, Indocyanine Green (ICG), and Methylene Blue (MB). This study aimed to assess and compare the penetration depth of these photosensitizers on the lateral surface of the root canal.
Materials and methods: The crown of 30 single-rooted teeth were separated by a diamond disc. The canals were prepared using a rotary system and were rinsed with 10 mL of 2.5% NaOCl. In order to remove the smear layer debris, 17% EDTA was placed in the root canal for 1 min, then rinsed with NaOCl and saline. The teeth were sterilized by autoclave and randomly assigned to three groups that filled with curcumin, ICG, or MB. Subsequently, they were incubated for 10 min and dried up by paper. Longitudinal sections were cut, and penetration depth of the photosensitizers in coronal, middle, and apical sections were measured using a stereomicroscope.
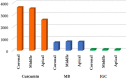
Results: Curcumin demonstrated a higher average penetration depth (3000 µm) than MB, and MB showed higher penetration depth than ICG. Significantly different penetration depths were observed in pairwise comparisons among all three groups (P<0.005).
Conclusion: Curcumin with its superior average penetration depth, emerges as a promising choice for effective root canal disinfection in endodontic treatments. Consideration of these findings may enhance the selection of photosensitizers in clinical applications.
Keywords: Curcumin; Indocyanine Green; Methylene Blue; Photodynamic Therapy; Photosensitizers.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The comparison of penetration depth of two different photosensitizers in root canals with and without smear layer: An in vitro study.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016 Mar;13:10-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 22. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016. PMID: 26592336
-
Penetration Depth of Sodium Hypochlorite in Dentinal Tubules after Conventional Irrigation, Passive Ultrasonic Agitation and Nd:YAG Laser Activated Irrigation.J Lasers Med Sci. 2016 Spring;7(2):105-11. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2016.18. Epub 2016 Mar 27. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27330706 Free PMC article.
-
Disinfection of radicular dentin using Riboflavin, Rose Bengal, Curcumin, and Porfimer sodium on extrusion bond strength of fiber post to radicular dentin.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2022 Mar;37:102625. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102625. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2022. PMID: 34781034
-
Comparing the Efficacy of Toluidine Blue, Methylene Blue and Curcumin in Photodynamic Therapy Against Enterococcus faecalis.J Lasers Med Sci. 2020 Fall;11(Suppl 1):S49-S54. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2020.S8. Epub 2020 Dec 30. J Lasers Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33995969 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Approach of High Technology Techniques for Control and Elimination of Endodontic Microbiota.J Lasers Med Sci. 2015 Fall;6(4):139-50. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2015.09. Epub 2015 Oct 27. J Lasers Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26705458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using photodynamic therapy for root canal disinfection during root canal therapy.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jul;19(3):1909-1910. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.03.018. Epub 2024 Mar 25. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39035288 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Influence of Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation of the Photosensitizer Used in Photodynamic Therapy on Microbial Reduction in the Root Canal System: An in Vitro Study.Iran Endod J. 2024;19(2):105-111. doi: 10.22037/iej.v19i2.36934. Iran Endod J. 2024. PMID: 38577000 Free PMC article.
-
Novel approaches on root canal disinfection methods against E. faecalis.J Oral Microbiol. 2025 Mar 6;17(1):2475947. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2025.2475947. eCollection 2025. J Oral Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40066376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bordea IR, Hanna R, Chiniforush N, Grădinaru E, Campian RS, Sirbu A, Amaroli A, Benedicenti S. Evaluation of the Outcome of Various Laser Therapy Applications in Root Canal Disinfection: A Systematic Review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020;29:101611. - PubMed
-
- Berutti E, Marini R, Angeretti A. Penetration Ability of Different Irrigants into Dentinal Tubules. J Endod. 1997;23(12):725–7. - PubMed
-
- Kouchi Y, Ninomiya J, Yasuda H, Fukui K, Moriyama T, Okamoto H. Location of Streptococcus Mutans in the Dentinal Tubules of Open Infected Root Canals. J Dent Res. 1980;59(12):2038–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous