Nucleolar detention of NONO shields DNA double-strand breaks from aberrant transcripts
- PMID: 38224452
- PMCID: PMC11014278
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae022
Nucleolar detention of NONO shields DNA double-strand breaks from aberrant transcripts
Abstract
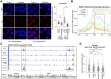
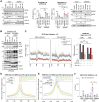
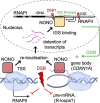
RNA-binding proteins emerge as effectors of the DNA damage response (DDR). The multifunctional non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein NONO/p54nrb marks nuclear paraspeckles in unperturbed cells, but also undergoes re-localization to the nucleolus upon induction of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). However, NONO nucleolar re-localization is poorly understood. Here we show that the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide stimulates the production of RNA polymerase II-dependent, DNA damage-inducible antisense intergenic non-coding RNA (asincRNA) in human cancer cells. Such transcripts originate from distinct nucleolar intergenic spacer regions and form DNA-RNA hybrids to tether NONO to the nucleolus in an RNA recognition motif 1 domain-dependent manner. NONO occupancy at protein-coding gene promoters is reduced by etoposide, which attenuates pre-mRNA synthesis, enhances NONO binding to pre-mRNA transcripts and is accompanied by nucleolar detention of a subset of such transcripts. The depletion or mutation of NONO interferes with detention and prolongs DSB signalling. Together, we describe a nucleolar DDR pathway that shields NONO and aberrant transcripts from DSBs to promote DNA repair.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





References
-
- Groelly F.J., Fawkes M., Dagg R.A., Blackford A.N., Tarsounas M.. Targeting DNA damage response pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2023; 23:78–94. - PubMed
-
- Marnef A., Legube G.. R-loops as Janus-faced modulators of DNA repair. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021; 23:305–313. - PubMed
-
- García-Muse T., Aguilera A. R loops: from physiological to pathological roles. Cell. 2019; 179:604–618. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

