Impact of rapid sequential combination therapy on distinct haemodynamic measures in newly diagnosed pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 38224960
- PMCID: PMC11098663
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14611
Impact of rapid sequential combination therapy on distinct haemodynamic measures in newly diagnosed pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
Aims: In pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), upfront combination therapy with ERA and PDE5i is associated with a reduction in morbidity and mortality events and improves standard haemodynamics, but data remain limited. Aims of this study were (i) to capture detailed haemodynamic effects of rapid sequential dual combination therapy in patients with newly diagnosed PAH; (ii) to monitor the impact of treatment initiation on clinical variables and patients' risk status, and (iii) to compare the treatment effect in patients with 'classical PAH' and 'PAH with co-morbidities'.
Methods: Fifty patients (median age 57 [42-71] years, 66% female) with newly diagnosed PAH (76% idiopathic) were treated with a PD5i/sGC-S or ERA, followed by addition of the respective other drug class within 4 weeks. All patients underwent repeat right heart catheterization (RHC) during early follow-up.
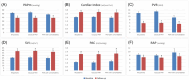
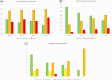
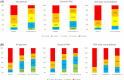
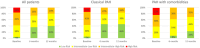
Results: At early repeat RHC (7 ± 2 months), there were substantial reductions in mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP: 52.2 ± 13.5 to 39.0 ± 10.6 mmHg; -25.3%), and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR: 12.1 ± 5.7 to 5.8 ± 3.1 WU; -52.1%), and an increase in cardiac index (2.1 ± 0.4 to 2.7 ± 0.7 mL/min/m2; +32.2%) (all P < 0.05). Haemodynamic improvements correlated with improved clinical parameters including 6-min walking distance (336 ± 315 to 389 ± 120 m), NTproBNP levels (1.712 ± 2.024 to 506 ± 550 ng/L, both P < 0.05) and WHO-FC at 12 months, resulting in improved risk status, and were found in patients with few (n = 37) or multiple cardiovascular co-morbidities (BMI > 30 kg/m2, hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease [≥3]; n = 13), albeit baseline PVR in PAH patients with multiple co-morbidities was lower (9.3 ± 4.4 vs. 13.1 ± 5.9 WU) and PVR reduction less pronounced compared with those with few co-morbidities (-42.7% vs. -54.7%). However, comprehensive haemodynamic assessment considering further variables of prognostic relevance such as stroke volume index and pulmonary artery compliance showed similar improvements among the two groups (SVI: +50.0% vs. +49.2%; PAC: 91.7% vs. 100.0%). Finally, the 4-strata risk assessment approach was better able to capture treatment response as compared with other approaches, particularly in patients with co-morbidities.
Conclusions: Rapid sequential combination therapy with PDE5i/sGC-S and ERA substantially ameliorates cardiopulmonary haemodynamics at early follow-up in patients without, and to a lesser extent, with cardiovascular co-morbidities. This occurs in line with improvements of clinical parameters and risk status.
Keywords: Combination therapy; Endothelin receptor antagonist; Haemodynamics; Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor; Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
© 2024 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Tilmann Kramer: Remunerations for lectures from Actelion. Felix Gerhardt: Remunerations for lectures from Actelion, Bayer, GSK, and United Therapeutics; grants to institution from Actelion, Bayer, Novartis, and United Therapeutics. Daniel Dumitrescu: Remunerations for lectures and/or consultancy from Actelion, Bayer, GSK, MSD, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Christopher Hohmann: Personal fees from MSD and Pfizer, lecture fees from Actelion, travel grants from Actelion, Bayer, Orion Pharma, and MSD. Stephan Rosenkranz: Remunerations for lectures and/or consultancy from Abbott, Acceleron, Actelion, Aerovate, Altavant, AOP, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, BMS, Ferrer, Gossamer, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, United Therapeutics, and Vifor; grants to institution from Actelion, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Janssen. The rest of the authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk Reduction and Hemodynamics with Initial Combination Therapy in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Feb 15;203(4):484-492. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1006OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 32857597
-
Changes in REVEAL risk score in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension treated with macitentan in clinical practice: results from the PRACMA study.BMC Pulm Med. 2020 Jun 2;20(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01197-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2020. PMID: 32487059 Free PMC article.
-
Early Addition of Selexipag to Double Therapy for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Sep 3;7(9):e2434691. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.34691. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 39312239 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Combination Therapy of Endothelin Receptor Antagonist and Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor on Clinical Outcome and Pulmonary Haemodynamics in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis.Clin Drug Investig. 2019 Nov;39(11):1031-1044. doi: 10.1007/s40261-019-00841-1. Clin Drug Investig. 2019. PMID: 31420854
-
Effectiveness and safety of endothelin receptor antagonists, alone and in combination therapy, in the pulmonary arterial hypertension-connective tissue disease subtype: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Oct;23(10):1276-1287. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13916. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32691518
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Gq inhibition induces strong pulmonary vasorelaxation and reverses pulmonary hypertension.EMBO Mol Med. 2024 Aug;16(8):1930-1956. doi: 10.1038/s44321-024-00096-0. Epub 2024 Jul 8. EMBO Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38977926 Free PMC article.
-
2024 update in heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Feb;12(1):8-42. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14857. Epub 2024 May 28. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 38806171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Providers' Behaviors, Attitudes, and Preferences on the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension With Endothelin Receptor Antagonist (ERA) + Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors (PDE5i).Pulm Circ. 2025 Jun 22;15(2):e70113. doi: 10.1002/pul2.70113. eCollection 2025 Apr. Pulm Circ. 2025. PMID: 40547449 Free PMC article.
-
Macitentan and Tadalafil Combination Therapy in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension and Cardiovascular Comorbidities: Real-World Evidence from OPUS and OrPHeUS.Adv Ther. 2025 Jul;42(7):3306-3333. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03180-0. Epub 2025 May 19. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40388087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lau EMT, Giannoulatou E, Celermajer DS, Humbert M. Epidemiology and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol 2017;14:603‐614. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin VV, Shah SJ, Souza R, Humbert M. Management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015;65:1976‐1997. - PubMed
-
- Lajoie AC, Lauzière G, Lega JC, Lacasse Y, Martin S, Simard S, et al. Combination therapy versus monotherapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension: A meta‐analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2016;4:291‐305. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

