Nanoscale silicate melt textures determine volcanic ash surface chemistry
- PMID: 38225238
- PMCID: PMC10789741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-44712-6
Nanoscale silicate melt textures determine volcanic ash surface chemistry
Abstract
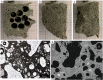
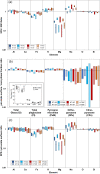
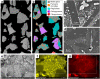
Explosive volcanic eruptions produce vast quantities of silicate ash, whose surfaces are subsequently altered during atmospheric transit. These altered surfaces mediate environmental interactions, including atmospheric ice nucleation, and toxic effects in biota. A lack of knowledge of the initial, pre-altered ash surface has required previous studies to assume that the ash surface composition created during magmatic fragmentation is equivalent to the bulk particle assemblage. Here we examine ash particles generated by controlled fragmentation of andesite and find that fragmentation generates ash particles with substantial differences in surface chemistry. We attribute this disparity to observations of nanoscale melt heterogeneities, in which Fe-rich nanophases in the magmatic melt deflect and blunt fractures, thereby focusing fracture propagation within aureoles of single-phase melt formed during diffusion-limited growth of crystals. In this manner, we argue that commonly observed pre-eruptive microtextures caused by disequilibrium crystallisation and/or melt unmixing can modify fracture propagation and generate primary discrepancies in ash surface chemistry, an essential consideration for understanding the cascading consequences of reactive ash surfaces in various environments.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Delmelle P, Wadsworth FB, Maters EC, Ayris PM. High temperature reactions between gases and ash particles in volcanic eruption plumes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2018;84:285–308. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2018.84.8. - DOI
-
- Umo, N. S. et al. The influence of chemical and mineral compositions on the parameterization of immersion freezing by volcanic ash particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 126, e2020JD033356 (2021).
-
- Cimarelli C, Genareau K. A review of volcanic electrification of the atmosphere and volcanic lightning. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2022;422:107449. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2021.107449. - DOI
-
- Óskarsson N. The interaction between volcanic gases and tephra: Fluorine adhering to tephra of the 1970 Hekla Eruption. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1980;8:251–266. doi: 10.1016/0377-0273(80)90107-9. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 653900/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 834225/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 247076/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 Ideas: European Research Council (FP7-IDEAS-ERC - Specific Programme: "Ideas" Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
- 19-IDS19-0083/National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- 364653263-TRR 235/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

