Efficacy of calcium hypochlorite in disinfection of gutta-percha cones contaminated with Candida albicans
- PMID: 38225531
- PMCID: PMC10920541
- DOI: 10.1007/s42770-024-01255-8
Efficacy of calcium hypochlorite in disinfection of gutta-percha cones contaminated with Candida albicans
Abstract
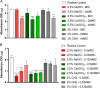
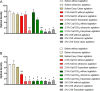
This study aimed to compare the efficacy of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 2.5% calcium hypochlorite [Ca(OCl)2], and 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) in the rapid disinfection of gutta-percha cones contaminated with Candida albicans. The minimum inhibitory and minimum fungicidal concentrations of each solution for C. albicans were determined and the ability of each solution to destroy and inhibit biofilm in culture wells was tested. In addition, ninety-eight gutta-percha cones contaminated with the fungal suspension were disinfected according to the type of solution (2.5% NaOCl, 2.5% Ca(OCl)2 or 2% CHX) in its different application methods (without agitation, ultrasonic agitation or agitation with Easy Clean), and regarding the exposure time to each irrigating solution (1 or 5 min). Next, the samples were checked for turbidity and evaluation of viable colonies. The compounds that showed the best performance in biofilm destruction were NaOCl and Ca(OCl)2 at a concentration of 2xMIC (p < 0.001). Regarding inhibited biofilm, the only compound that was effective at all MIC concentrations tested was 2.5% Ca(OCl)2 (p < 0.0001). Regarding the viable colonies, all solutions were effective concerning the control group, for all application methods, in 1 and 5 min (p < 0.05). The densitometer reading showed that CHX was the only effective solution in all application methods performed (p < 0.05). The results demonstrate that all tested solutions were effective in the rapid decontamination of cones contaminated with C. albicans.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Calcium hypochlorite; Chlorhexidine; Gutta-percha; Sodium hypochlorite.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Antimicrobial Efficacy of Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorhexidine in Gutta-Percha Cone Decontamination: A Systematic Review.Materials (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;18(7):1539. doi: 10.3390/ma18071539. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40271740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disinfection of gutta-percha cones with chlorhexidine and sodium hypochlorite.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005 Oct;100(4):512-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.10.002. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005. PMID: 16182174
-
Efficacy of peracetic acid in rapid disinfection of Resilon and gutta-percha cones compared with sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidine, and povidone-iodine.J Endod. 2013 Oct;39(10):1261-4. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.06.022. Epub 2013 Aug 16. J Endod. 2013. PMID: 24041388
-
Evaluation of residual antimicrobial effects and surface changes of gutta-percha disinfected with different solutions.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2011 Jan 1;12(1):47-51. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2011. PMID: 22186690
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Nanoparticle-Coated Gutta-Percha: A Systematic Review.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2025 Feb;35(2):213-220. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2025.02.213. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2025. PMID: 39936201
Cited by
-
The Antimicrobial Efficacy of Sodium Hypochlorite and Chlorhexidine in Gutta-Percha Cone Decontamination: A Systematic Review.Materials (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;18(7):1539. doi: 10.3390/ma18071539. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40271740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tomassini V, Pasdera O, Stefani P. Sterilizzazione dei coni di guttaperca: analisi della letteratura [Sterilization of gutta percha cones: analysis of the literature] G Stomatol Ortognatodonzia. 1986;5(4):61–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

