Kinematic movement and balance parameter analysis in neurological gait disorders
- PMID: 38225612
- PMCID: PMC10790442
- DOI: 10.1186/s13036-023-00398-w
Kinematic movement and balance parameter analysis in neurological gait disorders
Abstract
Background: Neurological gait disorders are mainly classified based on clinical observation, and therefore difficult to objectify or quantify. Movement analysis systems provide objective parameters, which may increase diagnostic accuracy and may aid in monitoring the disease course. Despite the increasing wealth of kinematic movement and balance parameter data, the discriminative value for the differentiation of neurological gait disorders is still unclear. We hypothesized that kinematic motion and balance parameter metrics would be differently altered across neurological gait disorders when compared to healthy controls.
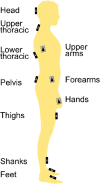
Methods: Thirty one patients (9 normal pressure hydrocephalus < NPH > , 16 cervical myelopathy < CM > , 6 lumbar stenosis < LST >) and 14 healthy participants were investigated preoperatively in an outpatient setting using an inertial measurement system (MyoMotion) during 3 different walking tasks (normal walking, dual-task walking with simultaneous backward counting, fast walking). In addition, the natural postural sway of participants was measured by pedobarography, with the eyes opened and closed. The range of motion (ROM) in different joint angles, stride time, as well as sway were compared between different groups (between-subject factor), and different task conditions (within-subject factor) by a mixed model ANOVA.
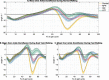
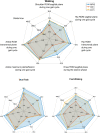
Results: Kinematic metrics and balance parameters were differently altered across different gait disorders compared to healthy controls. Overall, NPH patients significantly differed from controls in all movement parameters except for stride time, while they differed in balance parameters only with regard to AP movement. LST patients had significantly reduced ROMs of the shoulders, hips, and ankles, with significantly altered balance parameters regarding AP movement and passed center-of-pressure (COP) distance. CM patients differed from controls only in the ROM of the hip and ankle, but were affected in nearly all balance parameters, except for force distribution.
Conclusion: The application of inertial measurement systems and pedobarography is feasible in an outpatient setting in patients with different neurological gait disorders. Rather than defining singular discriminative values, kinematic gait and balance metrics may provide characteristic profiles of movement parameter alterations in the sense of specific ´gait signatures´ for different pathologies, which could improve diagnostic accuracy by defining objective and quantifiable measures for the discrimination of different neurological gait disorders.
Trial registration: The study was retrospectively registered on the 27th of March 2023 in the 'Deutsches Register für Klinische Studien' under the number DRKS00031555.
Keywords: Gait analysis; IMU; Pedobarography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Technological Advances for Gait and Balance in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;12(2):135. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12020135. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Assessment of Gait and Balance in Patients with Parkinson's Disease and Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2023 Jun 20;57(2):232-237. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2023.79990. eCollection 2023. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2023. PMID: 37899810 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy Verification of Spatio-Temporal and Kinematic Parameters for Gait Using Inertial Measurement Unit System.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Feb 29;20(5):1343. doi: 10.3390/s20051343. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32121456 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Validation of Non-Restrictive Inertial Gait Analysis of Individuals with Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury in Clinical Settings.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;22(11):4237. doi: 10.3390/s22114237. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684860 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Trends and Practices Toward Assessment and Rehabilitation of Neurodegenerative Disorders: Insights From Human Gait.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 15;16:859298. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.859298. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35495059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gait instability is a more specific predictor of corticospinal tract function than gait speed in clinically stable multiple sclerosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 23;15(1):26822. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10830-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40702042 Free PMC article.
-
Technological Advances for Gait and Balance in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;12(2):135. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12020135. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Gait Analysis Application for Assessing Upper and Lower Limb Movements to Detect Pathological Gait.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;24(19):6329. doi: 10.3390/s24196329. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gor-García-Fogeda MD, La Cano de Cuerda R, Carratalá Tejada M, Alguacil-Diego IM, Molina-Rueda F. Observational Gait Assessments in People With Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97:131–40. 10.1016/j.apmr.2015.07.018. - PubMed
-
- Toro B, Nester C, Farren P. A review of observational gait assessment in clinical practice. Physiother Theory Pract. 2003;19:137–149. doi: 10.1080/09593980307964. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

