Factors associated with the time required for CRP normalization in pyogenic spondylitis: A retrospective observational study
- PMID: 38225932
- PMCID: PMC10788255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xnsj.2023.100301
Factors associated with the time required for CRP normalization in pyogenic spondylitis: A retrospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Treatment for pyogenic spondylitis tends to be prolonged; however, few studies have examined the factors associated with the time required for infection control. Therefore, we analyzed a consecutive cohort of patients to identify factors associated with the time required to control infection in pyogenic spondylitis. This study aimed to clarify the factors linked to the duration necessary for achieving infection control in cases of pyogenic spondylitis, using C-reactive protein (CRP) normalization as an indicator.
Methods: In this retrospective observational study, we investigated 108 patients diagnosed with pyogenic spondylitis. We evaluated the number of days from the first visit to CRP normalization; for cases wherein CRP did not normalize, the number of days to the date of final blood sampling was evaluated. In the present study, infection control in pyogenic spondylitis was defined as a CRP falling within the normal range (≤0.14 mg/dL). We performed univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses to identify various factors associated with the time required for CRP normalization in pyogenic spondylitis.
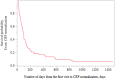
Results: The mean time required for CRP normalization was 148 days. Univariate Cox regression analysis showed that the serum creatinine level, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), lymphocyte percentage, neutrophil percentage, CRP level, CRP-albumin ratio, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio were significantly associated with the time required to control infection. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that a higher neutrophil percentage, diabetes mellitus, and a lower eGFR were the independent factors associated with a longer infection control time.
Conclusions: We found that a higher neutrophil percentage, diabetes mellitus, and a lower eGFR were significantly associated with a longer time for CRP normalization in pyogenic spondylitis. These findings may help identify patients with pyogenic spondylitis who are at a high risk for an extended infection control period.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Diabetes mellitus; Estimate glomerular filtration rate; Neutrophil; Risk factors; pyogenic spondylitis.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of conservative treatment for pyogenic spondylitis.Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017 Dec 20;1(3):135-139. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.1.2017-0009. eCollection 2017. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 31440624 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous endoscopic discectomy might be effective in selected cases of pyogenic spondylitis.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019 Sep-Dec;27(3):2309499019885446. doi: 10.1177/2309499019885446. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019. PMID: 31714174
-
Clinical outcomes of percutaneous curettage and continuous irrigation for pyogenic spondylitis.Surg Neurol. 2009 Nov;72(5):545-7; discussion 547. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2008.12.009. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Surg Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19608223
-
An infected aneurysm of the vertebral artery following cervical pyogenic spondylitis: a case report and literature review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Jan 6;22(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03881-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 33407352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for suspected primary and postoperative pyogenic spondylitis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jan 10;18(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03507-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36627651 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Factors prolonging antibiotic duration and impact of early surgery in thoracolumbar pyogenic spondylitis treated with minimally invasive posterior fixation.Eur Spine J. 2024 Dec;33(12):4672-4681. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08526-w. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 39417881
-
Cervical spine infection arising from chronic paronychia: A case report and review of literature.World J Orthop. 2024 Dec 18;15(12):1214-1225. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i12.1214. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39744732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hopkinson N, Stevenson J, Benjamin S. A case ascertainment study of septic discitis: clinical, microbiological and radiological features. QJM. 2001;94(9):465–470. - PubMed
-
- Kim YS, Kim JG, Yi J, et al. Changes in the medical burden of pyogenic and tuberculous spondylitis between 2007 and 2016: a nationwide cohort study. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;73:89–93. - PubMed
-
- Simon L, Gauvin F, Amre DK, Saint-Louis P, Lacroix J. Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as markers of bacterial infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(2):206–217. - PubMed
-
- von Dach E, Albrich WC, Brunel AS, et al. Effect of C-reactive protein-guided antibiotic treatment duration, 7-day treatment, or 14-day treatment on 30-day clinical failure rate in patients with uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020;323(21):2160–2169. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous