Biochanin A attenuates spinal cord injury in rats during early stages by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammasome activation
- PMID: 38227535
- PMCID: PMC11040286
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.390953
Biochanin A attenuates spinal cord injury in rats during early stages by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammasome activation
Abstract
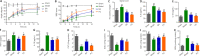
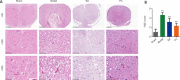
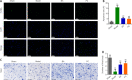
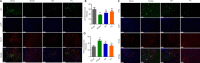
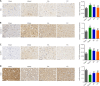
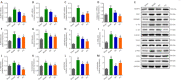
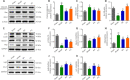
JOURNAL/nrgr/04.03/01300535-202409000-00038/figure1/v/2024-01-16T170235Z/r/image-tiff Previous studies have shown that Biochanin A, a flavonoid compound with estrogenic effects, can serve as a neuroprotective agent in the context of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury; however, its effect on spinal cord injury is still unclear. In this study, a rat model of spinal cord injury was established using the heavy object impact method, and the rats were then treated with Biochanin A (40 mg/kg) via intraperitoneal injection for 14 consecutive days. The results showed that Biochanin A effectively alleviated spinal cord neuronal injury and spinal cord tissue injury, reduced inflammation and oxidative stress in spinal cord neurons, and reduced apoptosis and pyroptosis. In addition, Biochanin A inhibited the expression of inflammasome-related proteins (ASC, NLRP3, and GSDMD) and the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway, activated the Nrf2/heme oxygenase 1 signaling pathway, and increased the expression of the autophagy markers LC3 II, Beclin-1, and P62. Moreover, the therapeutic effects of Biochanin A on early post-spinal cord injury were similar to those of methylprednisolone. These findings suggest that Biochanin A protected neurons in the injured spinal cord through the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor κB and Nrf2/heme oxygenase 1 signaling pathways. These findings suggest that Biochanin A can alleviate post-spinal cord injury at an early stage.
Copyright © 2024 Copyright: © 2024 Neural Regeneration Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lupenone improves motor dysfunction in spinal cord injury mice through inhibiting the inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in microglia via the nuclear factor kappa B pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Aug 1;19(8):1802-1811. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.389302. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38103247 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin alleviates spinal cord injury by inhibiting nerve cell ferroptosis through upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):2041-2049. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390960. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38227534 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperetin ameliorates spinal cord injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis through enhancing Nrf2 signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 May;118:110103. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110103. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37001385
-
Biochanin A Provides Neuroprotection Against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Nrf2-Mediated Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Signaling Pathway in Rats.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 26;25:8975-8983. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918665. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31767824 Free PMC article.
-
Role of pyroptosis in spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications.J Adv Res. 2020 Aug 18;28:97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.08.004. eCollection 2021 Feb. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 33364048 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in spinal cord organoid research: advancing understanding of neural development, disease modelling, and regenerative medicine.Biomater Transl. 2024 Nov 15;5(4):355-371. doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2024.04.003. eCollection 2024. Biomater Transl. 2024. PMID: 39872925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bletilla striata polysaccharide induces autophagy through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to promote the survival of cross-boundary flap in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 10;16:1544932. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1544932. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40129948 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into Nrf2-driven pathogenesis and therapeutic targeting in spinal cord injury.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 10;16:1574834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1574834. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40709178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of FOXD3 O-GlcNAc Modification Ameliorates Spinal Cord Injury by Promoting STUB1-Mediated Ubiquitination Degradation of HMGB1.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Sep;62(9):11268-11285. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04954-x. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40272767
-
Flavonoids regulating NLRP3 inflammasome: a promising approach in alleviating diabetic peripheral neuropathy.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May;33(5):2231-2262. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01729-7. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40205269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Wahab BA, Alkahtani SA, Elagab EAM. Tadalafil alleviates cisplatin-induced reproductive toxicity through the activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and the inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in male rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2020;96:165–174. - PubMed
-
- Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12:1–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

