Feasibility of Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Patients with Follicular Lymphoma
- PMID: 38228081
- PMCID: PMC11261198
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2023.869
Feasibility of Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Patients with Follicular Lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: The feasibility of sequencing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in plasma as a biomarker to predict early relapse or poor prognosis in patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) receiving systemic immunochemotherapy is not clear.
Materials and methods: We sequenced DNA from cell-free plasma that was serially obtained from newly diagnosed FL patients undergoing systemic immunochemotherapy. The mutation profiles of ctDNA at the time of diagnosis and at response evaluation and relapse and/or progression were compared with clinical course and treatment outcomes.
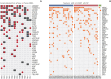
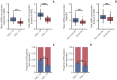
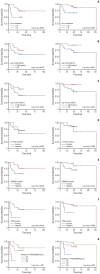
Results: Forty samples from patients receiving rituximab-containing immunochemotherapy were analyzed. Baseline sequencing detected mutations in all cases, with the major detected mutations being KMT2C (50%), CREBBP (45%), and KMT2D (45%). The concentration of ctDNA and tumor mutation burden showed a significant association with survival outcome. In particular, the presence of mutations in CREBBP and TP53 showed poor prognosis compared with patients without them. Longitudinal analysis of ctDNA using serially collected plasma samples showed an association between persistence or reappearance of ctDNA mutations and disease relapse or progression.
Conclusion: Analysis of ctDNA mutations in plasma at diagnosis might help predict outcome of disease, while analysis during follow-up may help to monitor disease status of patients with advanced FL. However, the feasibility of ctDNA measurement must be improved in order for it to become an appropriate and clinically relevant test in FL patients.
Keywords: Circulating tumor DNA; Follicular lymphoma; Mutations; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating tumor DNA as a powerful tool in diagnostics and treatment outcome prediction - focus on large B-cell lymphomas and follicular lymphomas.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2025 Jun;25(6):275-295. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2025.2500659. Epub 2025 May 22. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2025. PMID: 40326242 Review.
-
The prognostic value of clonal heterogeneity and quantitative assessment of plasma circulating clonal IG-VDJ sequences at diagnosis in patients with follicular lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8765-8774. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14448. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28060738 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Personalized monitoring of circulating tumor DNA with a specific signature of trackable mutations after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in follicular lymphoma patients.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 5;14:1188818. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188818. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37342332 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the evolution of untreated high-intermediate/high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by circulating tumour DNA.Br J Haematol. 2022 Feb;196(3):617-628. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17894. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Br J Haematol. 2022. PMID: 34664256
-
[Progression and application of circulating tumor DNA in lymphoma].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Sep 14;45(9):878-882. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121090-20240528-00197. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39414617 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Molecular Biomarkers in Prediction of High-Grade Transformation and Outcome in Patients with Follicular Lymphoma: A Comprehensive Systemic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11179. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011179. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456961 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Circulating Tumor DNA Detection in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients With Central Nervous System Involvement in Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Ann Lab Med. 2025 Jan 1;45(1):90-95. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0257. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Ann Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39344147 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathology of lymphoma and its treatment strategies: from mechanistic elucidation to precision medicine.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 9;16:1620895. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620895. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40703518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating tumor DNA in lymphoma: technologies and applications.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 Mar 11;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01673-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40069858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:443–59. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Ghielmini M, Rule S, Salles G, Vitolo U, Ladetto M, et al. Newly diagnosed and relapsed follicular lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:v83–90. - PubMed
-
- Hiddemann W, Kneba M, Dreyling M, Schmitz N, Lengfelder E, Schmits R, et al. Frontline therapy with rituximab added to the combination of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) significantly improves the outcome for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma compared with therapy with CHOP alone: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2005;106:3725–32. - PubMed
-
- Marcus R, Imrie K, Solal-Celigny P, Catalano JV, Dmoszynska A, Raposo JC, et al. Phase III study of R-CVP compared with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone alone in patients with previously untreated advanced follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4579–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

