Targeted inhibition of the HNF1A/SHH axis by triptolide overcomes paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38228910
- PMCID: PMC11053095
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-023-01219-y
Targeted inhibition of the HNF1A/SHH axis by triptolide overcomes paclitaxel resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
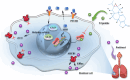
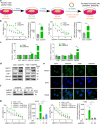
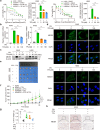
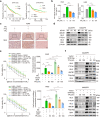
Paclitaxel resistance is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, and currently, there is no promising drug for paclitaxel resistance. In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying the chemoresistance in human NSCLC-derived cell lines. We constructed paclitaxel-resistant NSCLC cell lines (A549/PR and H460/PR) by long-term exposure to paclitaxel. We found that triptolide, a diterpenoid epoxide isolated from the Chinese medicinal herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, effectively enhanced the sensitivity of paclitaxel-resistant cells to paclitaxel by reducing ABCB1 expression in vivo and in vitro. Through high-throughput sequencing, we identified the SHH-initiated Hedgehog signaling pathway playing an important role in this process. We demonstrated that triptolide directly bound to HNF1A, one of the transcription factors of SHH, and inhibited HNF1A/SHH expression, ensuing in attenuation of Hedgehog signaling. In NSCLC tumor tissue microarrays and cancer network databases, we found a positive correlation between HNF1A and SHH expression. Our results illuminate a novel molecular mechanism through which triptolide targets and inhibits HNF1A, thereby impeding the activation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway and reducing the expression of ABCB1. This study suggests the potential clinical application of triptolide and provides promising prospects in targeting the HNF1A/SHH pathway as a therapeutic strategy for NSCLC patients with paclitaxel resistance. Schematic diagram showing that triptolide overcomes paclitaxel resistance by mediating inhibition of the HNF1A/SHH/ABCB1 axis.
Keywords: ABCB1; HNF1A; Sonic Hedgehog; non-small cell lung cancer; paclitaxel resistance; triptolide.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

