METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS): a quality scoring tool for radiomics research endorsed by EuSoMII
- PMID: 38228979
- PMCID: PMC10792137
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-023-01572-w
METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS): a quality scoring tool for radiomics research endorsed by EuSoMII
Abstract
Purpose: To propose a new quality scoring tool, METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS), to assess and improve research quality of radiomics studies.
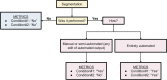
Methods: We conducted an online modified Delphi study with a group of international experts. It was performed in three consecutive stages: Stage#1, item preparation; Stage#2, panel discussion among EuSoMII Auditing Group members to identify the items to be voted; and Stage#3, four rounds of the modified Delphi exercise by panelists to determine the items eligible for the METRICS and their weights. The consensus threshold was 75%. Based on the median ranks derived from expert panel opinion and their rank-sum based conversion to importance scores, the category and item weights were calculated.
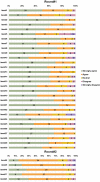
Result: In total, 59 panelists from 19 countries participated in selection and ranking of the items and categories. Final METRICS tool included 30 items within 9 categories. According to their weights, the categories were in descending order of importance: study design, imaging data, image processing and feature extraction, metrics and comparison, testing, feature processing, preparation for modeling, segmentation, and open science. A web application and a repository were developed to streamline the calculation of the METRICS score and to collect feedback from the radiomics community.
Conclusion: In this work, we developed a scoring tool for assessing the methodological quality of the radiomics research, with a large international panel and a modified Delphi protocol. With its conditional format to cover methodological variations, it provides a well-constructed framework for the key methodological concepts to assess the quality of radiomic research papers.
Critical relevance statement: A quality assessment tool, METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS), is made available by a large group of international domain experts, with transparent methodology, aiming at evaluating and improving research quality in radiomics and machine learning.
Key points: • A methodological scoring tool, METRICS, was developed for assessing the quality of radiomics research, with a large international expert panel and a modified Delphi protocol. • The proposed scoring tool presents expert opinion-based importance weights of categories and items with a transparent methodology for the first time. • METRICS accounts for varying use cases, from handcrafted radiomics to entirely deep learning-based pipelines. • A web application has been developed to help with the calculation of the METRICS score ( https://metricsscore.github.io/metrics/METRICS.html ) and a repository created to collect feedback from the radiomics community ( https://github.com/metricsscore/metrics ).
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Guideline; Machine learning; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies:
AAB: CEO and shareholder of Quibim SL. Editorial Board Member of Insights into Imaging. BB: Founder and CEO of Lernrad GmbH, speaker bureau Bayer Vital GmbH.
EK: Speaker fees for Siemens Healthineers, speaker fees for Abbvie, member of the scientific advisory board and shareholder of contextflow GmbH, Vienna. Member of the scientific advisory board Gleamer.
RoC: Support for attending meetings from Bracco and Bayer; research collaboration with Siemens Healthcare; co-funding by the European Union - FESR or FSE, PON Research and Innovation 2014-2020 - DM 1062/2021. Editorial Board Member of Insights into Imaging.
LF: Speaker fees: Bayer, Novartis, Janssen, Sanofi, GE Healthcare, Fujifilm, ESGAR, C-FIM, Median Technologies, Vestfold Hospital. Scientific committee: Institut Servier. Research collaboration/grants: Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Philips, Evolucare, ArianaPharma, Dassault Systems. Traveling support: Guerbet.
LSF: General Electric Healthcare (Honoraria), Median Technologies (Honoraria), Sanofi (Honoraria), Guerbet (conference funding), Bristol-Myers Squibb (research grant).
MEK: Meeting attendance support from Bayer.
LMB: Editor-in-Chief of Insights into Imaging, member of the non-profit Scientific Advisory Boards of Quibim SL and the Girona Biomedical Research Institute.
DPdS: Editorial Board Member of Insights into Imaging. Speaker fees for Bayer AG, Advisory Board for cook medical, author fees for AMBOSS GmbH.
AP: Editorial board member of Insights into Imaging.
FV: None related to this study; received support to attend meetings from Bracco Imaging S.r.l., and GE Healthcare.
FS: has received research grants from Bayer Healthcare, Bracco, and General Electric Healthcare.
None of the authors related to the Insights into Imaging Editorial team and Editorial Board has taken part in the review process of this article.
Other authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures







References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

