Molecular evolution analysis of MYB5 in Brassicaceae with specific focus on seed coat color of Brassica napus
- PMID: 38229007
- PMCID: PMC10790415
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-023-04718-6
Molecular evolution analysis of MYB5 in Brassicaceae with specific focus on seed coat color of Brassica napus
Abstract
Background: MYB transcription factors are splay a vital role in plant biology, with previous research highlighting the significant impact of the R2R3-MYB-like transcription factor MYB5 on seed mucilage biosynthesis, trichome branching, and seed coat development. However, there is a dearth of studies investigating its role in the regulation of proanthocyanidin (PA) biosynthesis.
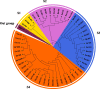
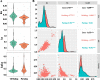
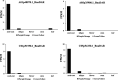
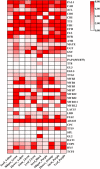
Results: In this study, a total of 51 MYB5 homologous genes were identified across 31 species belonging to the Brassicaceae family, with particular emphasis on Brassica napus for subsequent investigation. Through phylogenetic analysis, these genes were categorized into four distinct subclasses. Protein sequence similarity and identity analysis demonstrated a high degree of conservation of MYB5 among species within the Brassicaceae family. Additionally, the examination of selection pressure revealed that MYB5 predominantly underwent purifying selection during its evolutionary history, as indicated by the Ka/Ks values of all MYB5 homologous gene pairs being less than one. Notably, we observed a higher rate of non-synonymous mutations in orthologous genes compared to paralogous genes, and the Ka/Ks value displayed a stronger correlation with Ka. In B. napus, an examination of expression patterns in five tissues revealed that MYB5 exhibited particularly high expression in the black seed coat. The findings from the WGCNA demonstrated a robust correlation between MYB5 and BAN(ANR) associated with PA biosynthesis in the black seed coat, providing further evidence of their close association and co-expression. Furthermore, the results obtained from of the analysis of protein interaction networks offer supplementary support for the proposition that MYB5 possesses the capability to interact with transcriptional regulatory proteins, specifically TT8 and TT2, alongside catalytic enzymes implicated in the synthesis of PAs, thereby making a contribution to the biosynthesis of PAs. These findings imply a plausible and significant correlation between the nuique expression pattern of MYB5 and the pigmentation of rapeseed coats. Nevertheless, additional research endeavors are imperative to authenticate and substantiate these findings.
Conclusions: This study offers valuable insights into the genetic evolution of Brassicaceae plants, thereby serving as a significant reference for the genetic enhancement of Brassicaceae seed coat color.
Keywords: Brassica napus; Brassicaceae; Homologous gene; MYB5; Seed coat.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the anthocyanin-related genes during seed coat development in six Brassica species.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 9;24(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09170-2. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36894869 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing of BnTT10 family genes causes retarded pigmentation and lignin reduction in the seed coat of Brassica napus.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 22;8(4):e61247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061247. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23613820 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis MYB5 transcription factor regulates mucilage synthesis, seed coat development, and trichome morphogenesis.Plant Cell. 2009 Jan;21(1):72-89. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.063503. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19136646 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary studies of the bHLH transcription factors belonging to MBW complex: their role in seed development.Ann Bot. 2023 Nov 23;132(3):383-400. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad097. Ann Bot. 2023. PMID: 37467144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of manipulating seed coat coloration in oilseed Brassica species.J Appl Genet. 2013 May;54(2):135-45. doi: 10.1007/s13353-012-0132-y. Epub 2013 Jan 18. J Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23329015 Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-genome analysis of the R2R3-MYB genes family in Brassica napus unveils phylogenetic divergence and expression profiles under hormone and abiotic stress treatments.Front Plant Sci. 2025 May 23;16:1588362. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1588362. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40487211 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study on Cowpea seed coat color using RGB images.Mol Breed. 2024 Nov 19;44(12):80. doi: 10.1007/s11032-024-01516-2. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mol Breed. 2024. PMID: 39574799
References
-
- Paz-Ares J, Ghosal D, Wienand U, Peterson PA, Saedler H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. Embo J. 1987;6(12):3553–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02684.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- YC2022-s929/Jiangxi Province Postgraduate Innovation Special Fund Project
- YC2022-s929/Jiangxi Province Postgraduate Innovation Special Fund Project
- 20223BBF61002/Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province
- 20223BBF61002/Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province
- 20223BBF61002/Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province
- 20223BBF61002/Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province
- 20223BBF61002/Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province
- YLKFKT202202/Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Oilcrops Biology
- YLKFKT202202/Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Oilcrops Biology
- YLKFKT202202/Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Oilcrops Biology
- YLKFKT202202/Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Oilcrops Biology
- YLKFKT202202/Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Oilcrops Biology
- 20224BAB215016/Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

