Proteome profiling of enriched membrane-associated proteins unraveled a novel sophorose and cello-oligosaccharide transporter in Trichoderma reesei
- PMID: 38229067
- PMCID: PMC10790555
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-023-02279-9
Proteome profiling of enriched membrane-associated proteins unraveled a novel sophorose and cello-oligosaccharide transporter in Trichoderma reesei
Abstract
Background: Trichoderma reesei is an organism extensively used in the bioethanol industry, owing to its capability to produce enzymes capable of breaking down holocellulose into simple sugars. The uptake of carbohydrates generated from cellulose breakdown is crucial to induce the signaling cascade that triggers cellulase production. However, the sugar transporters involved in this process in T. reesei remain poorly identified and characterized.
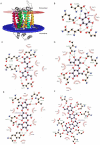
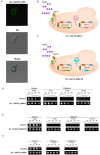
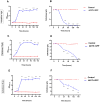
Results: To address this gap, this study used temporal membrane proteomics analysis to identify five known and nine putative sugar transporters that may be involved in cellulose degradation by T. reesei. Docking analysis pointed out potential ligands for the putative sugar transporter Tr44175. Further functional validation of this transporter was carried out in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The results showed that Tr44175 transports a variety of sugar molecules, including cellobiose, cellotriose, cellotetraose, and sophorose.
Conclusion: This study has unveiled a transporter Tr44175 capable of transporting cellobiose, cellotriose, cellotetraose, and sophorose. Our study represents the first inventory of T. reesei sugar transportome once exposed to cellulose, offering promising potential targets for strain engineering in the context of bioethanol production.
Keywords: Cellulose; Membrane-associated proteome; Sugar transporters; Trichoderma reesei.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have any conflicting of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zabed H, Sahu JN, Suely A, Boyce AN, Faruq G. Bioethanol production from renewable sources: current perspectives and technological progress. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;71:1–27. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.076. - DOI
-
- Castro LDS, Antoniêto ACC, Pedersoli WR, Silva-Rocha R, Persinoti GF, Silva RN. Expression pattern of cellulolytic and xylanolytic genes regulated by transcriptional factors XYR1 and CRE1 are affected by carbon source in Trichoderma reesei. Gene Expr Patterns. 2014;14:88–95. doi: 10.1016/j.gep.2014.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

