Current status of autologous breast reconstruction in Europe: how to reduce donor site morbidity
- PMID: 38229849
- PMCID: PMC10788572
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-23-288
Current status of autologous breast reconstruction in Europe: how to reduce donor site morbidity
Abstract
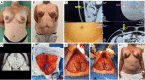
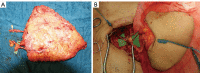
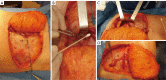
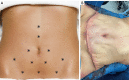
Autologous reconstruction techniques for breast reconstruction have significantly evolved in the last few decades in Europe. In the search of reducing the donor site morbidity, surgeons explored the possibilities to preserve the rectus muscle and its function, and a transition to deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flaps was started in the nineties. Throughout the years, and especially in the last decade, we have increasingly implemented aesthetic refinements for donor site handling in DIEP flap breast reconstruction. In our practice, autologous breast reconstruction provides an opportunity to effectively remodel the donor site, minimising functional morbidity, and maximising aesthetic satisfaction. To achieve this, careful patient selection, pre-operative preparation, meticulous intra-operative dissection, and a clear post-operative protocol are essential. The main goal in autologous breast reconstruction, and its biggest advantage, is to offer the patient a natural look and feel of the reconstructed breast. A second goal is to minimize the number of procedures needed to reach the desired breast shape, size, and volume. In most patients, the number of operations ranges between one and three. The third main goal is to minimize the donor site morbidity, both functionally and aesthetically. Functionally, this implies preserving as much of the rectus abdominis muscle as possible, limiting the fascia incision, preserving the motor branches to the muscle, ensuring an adequate fascial closure, and repairing the rectus diastasis is present. Aesthetically, we aim to have a low position of the scar, an aesthetically pleasing location of the umbilicus, and limited or no lateral skin excess or so called "dogears". In this clinical practice review article, we provide an overview of current autologous reconstruction methods, with a focus on minimising donor site morbidity and enhancing the aesthetic result of the donor site. We discuss key concepts in autologous reconstruction and provide surgical pearls for performing the procedure effectively with optimal reconstructive and aesthetic result.
Keywords: Autologous reconstruction; abdominoplasty deep inferior epigastric perforator flap (abdominoplasty DIEP flap); aesthetic donor site closure.
2023 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-23-288/coif). The series “Hot Topics in Breast Reconstruction World Wide” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. M.H. reports that he serves as the National Expert for the Superior Council in Belgian Minister of Health (MoH) and is a consultant to Polytech for scientific activities. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
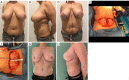
References
-
- Mühlbauer W, Olbrisch R. The latissimus dorsi myo-cutaneous flap for breast reconstruction. Chir Plastica 1977;4:27-34.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
