YTHDF2-regulated matrilin-3 mitigates post-reperfusion hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke via the PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 38230623
- PMCID: PMC10880072
- DOI: 10.1093/jnen/nlad102
YTHDF2-regulated matrilin-3 mitigates post-reperfusion hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke via the PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
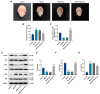
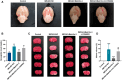
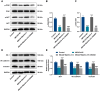
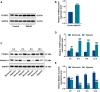
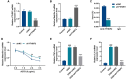
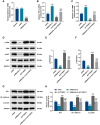
Hemorrhagic transformation can complicate ischemic strokes after recanalization treatment within a time window that requires early intervention. To determine potential therapeutic effects of matrilin-3, rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion was produced using transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO); intracranial hemorrhage and infarct volumes were assayed through hemoglobin determination and 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazoliumchloride (TTC) staining, respectively. Oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) modeling of ischemia was performed on C8-D1A cells. Interactions between matrilin-3 and YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein F2 (YTHDF2) were determined using RNA immunoprecipitation assay and actinomycin D treatment. Reperfusion after tMCAO modeling increased hemorrhage, hemoglobin content, and infarct volumes; these were alleviated by matrilin treatment. Matrilin-3 was expressed at low levels and YTHDF2 was expressed at high levels in ischemic brains. In OGD-induced cells, matrilin-3 was negatively regulated by YTHDF2. Matrilin-3 overexpression downregulated p-PI3K/PI3K, p-AKT/AKT, ZO-1, VE-cadherin and occludin, and upregulated p-JNK/JNK in ischemic rat brains; these effects were reversed by LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor). YTHDF2 knockdown inactivated the PI3K/AKT pathway, inhibited inflammation and decreased blood-brain barrier-related protein levels in cells; these effects were reversed by matrilin-3 deficiency. These results indicate that YTHDF2-regulated matrilin-3 protected ischemic rats against post-reperfusion hemorrhagic transformation via the PI3K/AKT pathway and that matrilin may have therapeutic potential in ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Hemorrhagic transformation; Ischemic stroke; Matrilin-3; PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein F2.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Association of Neuropathologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no duality or conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FGF17 protects cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced blood-brain barrier disruption via FGF receptor 3-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 May 15;971:176521. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176521. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38522639
-
The neuroprotective effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 via the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway are mediated by the PI3K/AKT cascade following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Brain Res Bull. 2021 Dec;177:373-387. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.10.017. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Brain Res Bull. 2021. PMID: 34717965
-
HACE1 exerts a neuroprotective role against oxidative stress in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 pathway.Neuroscience. 2024 Nov 1;559:249-262. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.09.002. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Neuroscience. 2024. PMID: 39244008
-
Pharmacological modulation of PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR/ERK signaling pathways in ischemic injury: a mechanistic perspective.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Feb 26;40(3):131. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01543-8. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40009091 Review.
-
The Role of Progranulin (PGRN) in the Pathogenesis of Ischemic Stroke.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3435-3447. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01396-8. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37561339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactylation and Ischemic Stroke: Research Progress and Potential Relationship.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May;62(5):5359-5376. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04624-4. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39541071 Review.
-
Enhancement of YTHDF2 plays a protective role in acute IRI models through downregulation of TUG1 expression.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0319605. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319605. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40273066 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of the m6A reader YTHDF2 in the maintenance and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells. 2025 Jun 24;43(7):sxaf032. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxaf032. Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40418739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen S, Lu X, Zhang W, et al.Does prior antiplatelet treatment increase the risk of hemorrhagic transformation and unfavorable outcome on day 90 after intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke patients? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2016;25:1366–70 - PubMed
-
- Momosaki R, Yasunaga H, Kakuda W, et al.Very early versus delayed rehabilitation for acute ischemic stroke patients with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. Cerebrovasc Dis 2016;42:41–8 - PubMed
-
- Roth C, Papanagiotou P, Behnke S, et al.Stent-assisted mechanical recanalization for treatment of acute intracerebral artery occlusions. Stroke 2010;41:2559–67 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

