The aminosalicylate - folate connection
- PMID: 38230664
- PMCID: PMC11305456
- DOI: 10.1080/03602532.2024.2303507
The aminosalicylate - folate connection
Abstract
Two aminosalicylate isomers have been found to possess useful pharmacological behavior: p-aminosalicylate (PAS, 4AS) is an anti-tubercular agent that targets M. tuberculosis, and 5-aminosalicylate (5AS, mesalamine, mesalazine) is used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC) and other inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). PAS, a structural analog of pABA, is biosynthetically incorporated by bacterial dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS), ultimately yielding a dihydrofolate (DHF) analog containing an additional hydroxyl group in the pABA ring: 2'-hydroxy-7,8-dihydrofolate. It has been reported to perturb folate metabolism in M. tuberculosis, and to selectively target M. tuberculosis dihydrofolate reductase (mtDHFR). Studies of PAS metabolism are reviewed, and possible mechanisms for its mtDHFR inhibition are considered. Although 5AS is a more distant structural relative of pABA, multiple lines of evidence suggest a related role as a pABA antagonist that inhibits bacterial folate biosynthesis. Structural data support the likelihood that 5AS is recognized by the DHPS pABA binding site, and its effects probably range from blocking pABA binding to formation of a dead-end dihydropterin-5AS adduct. These studies suggest that mesalamine acts as a gut bacteria-directed antifolate, that selectively targets faster growing, more folate-dependent species.
Keywords: 5-aminosalicylate; Ulcerative colitis; inflammatory bowel disease; mesalamine; p-aminosalicylate; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The Author declares that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

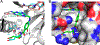
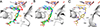

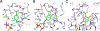


References
-
- Allgayer H 2003. ‘Review article: mechanisms of action of mesalazine in preventing colorectal carcinoma in inflammatory bowel disease’, Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 18 Suppl 2: 10–4. - PubMed
-
- Allgayer H, Sonnenbichler J, Kruis W, and Paumgartner G. 1985. ‘Determination of the pK values of 5-aminosalicylic acid and N-acetylaminosalicylic acid and comparison of the pH dependent lipid-water partition coefficients of sulphasalazine and its metabolites’, Arzneimittelforschung, 35: 1457–9. - PubMed
-
- Andersen T, Hvid M, Johansen C, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Hetland ML, Horslev-Petersen K, Junker P, Ostergaard M, and Deleuran B. 2015. ‘Interleukin-23 in early disease development in rheumatoid arthritis’, Scand J Rheumatol, 44: 438–42. - PubMed
-
- Ariens EJ, and Simonis AM. 1955. ‘The biosynthesis of folic-acid homologues from amino-carboxy-pyridine and other para-aminobenzoic-acid substitutes by E. coli’, Schweiz Z Pathol Bakteriol, 18: 71–80. - PubMed
-
- Auletta AE, Gery AM, Parmar A, Davis J, Mishra L, and Mead JA. 1974. ‘The effect of folate and folate analogs upon dihydrofolate reductase and DNA synthesis in kidneys of normal mice’, Life Sci, 14: 1541–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
