Edible Insects: Perceptions of Marketing, Economic, and Social Aspects among Citizens of Different Countries
- PMID: 38231666
- PMCID: PMC10706764
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12234229
Edible Insects: Perceptions of Marketing, Economic, and Social Aspects among Citizens of Different Countries
Abstract
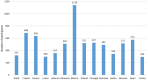
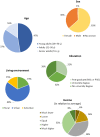
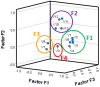
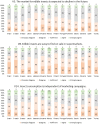
Because edible insects (EI) have been, in recent years, recommended as a nutritious animal protein food with enormous environmental advantages over other sources of animal protein for human consumption, studies aimed at investigating the consumer perspective have become more prominent. Hence, this study intended to examine the perceptions of participants from different countries about the commercialization and economic and social impacts of edible insects. The study was made using a questionnaire survey, and data were collected in Brazil, Croatia, Greece, Latvia, Lebanon, Lithuania, Mexico, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, and Turkey. The final number of received answers was 7222 participants. For the treatment of the results, different statistical techniques were used: factor analysis, internal reliability by Cronbach's alpha, cluster analysis, ANOVA to test differences between groups, and Chi-square tests. The results obtained confirmed the validity of the scale, constituted by 12 out of the 14 items initially considered, distributed by 4 factors: the first related to the economic impact of EIs, the second related to the motivation for consumption of EIs, the third related to the places of purchase of EIs, and the fourth corresponding to a question presented to the participants as a false statement. A cluster analysis allowed identifying three clusters, with significant differences between them according to all the sociodemographic variables tested. Also, it was found that the participants expressed an exceptionally high level of agreement with aspects such as the difficulty in finding EIs on sale, knowledge acting as a strong motivator for EI consumption, and the role of personalities and influencers in increasing the will to consume EIs. Finally, practically all sociodemographic variables were found to be significantly associated with perceptions (country, sex, education, living environment, and income), but not age. In conclusion, the perceptions about EI commercialization were investigated and revealed differences among samples originating from different countries. Moreover, the sociodemographic characteristics of the participants were found to be strongly associated with their perceptions.
Keywords: economy; insect consumption; marketing; questionnaire survey; social impact.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Emel Damarli was employed by the company Research and Development Center, Altıparmak Food Coop., Çekmeköy, 34782 İstanbul, Turkey. This author's contribution is investigation. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Edible Insects: Consumption, Perceptions, Culture and Tradition Among Adult Citizens from 14 Countries.Foods. 2024 Oct 25;13(21):3408. doi: 10.3390/foods13213408. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39517192 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Questionnaire to Assess Knowledge and Perceptions about Edible Insects.Insects. 2021 Dec 31;13(1):47. doi: 10.3390/insects13010047. Insects. 2021. PMID: 35055890 Free PMC article.
-
Edible Insects: Preliminary Study about Perceptions, Attitudes, and Knowledge on a Sample of Portuguese Citizens.Foods. 2021 Mar 26;10(4):709. doi: 10.3390/foods10040709. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33810486 Free PMC article.
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Motivations for Consumption of Edible Insects: A Systematic Review.Foods. 2022 Nov 15;11(22):3643. doi: 10.3390/foods11223643. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36429235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sustainable Protein Sources: Functional Analysis of Tenebrio molitor Hydrolysates and Attitudes of Consumers in Poland and Spain Toward Insect-Based Foods.Foods. 2025 Jan 20;14(2):333. doi: 10.3390/foods14020333. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39856998 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Nutritional and Functional Properties of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae and Isolated Soy Protein Mixtures as Alternative Protein Sources.Foods. 2024 May 15;13(10):1540. doi: 10.3390/foods13101540. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38790840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UN Sustainable Development Goals|United Nations Development Programme. [(accessed on 22 August 2023)]. Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals.
-
- Mejía G., Aránguiz R., Espejo-Díaz J.A., Granados-Rivera D., Mejía-Argueta C. Can Street Markets Be a Sustainable Strategy to Mitigate Food Insecurity in Emerging Countries? Insights from a Competitive Facility Location Model. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023;86:101456. doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2022.101456. - DOI
-
- Fusco G., Campobasso F., Laureti L., Frittelli M., Valente D., Petrosillo I. The Environmental Impact of Agriculture: An Instrument to Support Public Policy. Ecol. Indic. 2023;147:109961. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109961. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

