Green Extraction of Hodgsonia heteroclita Oilseed Cake Powder to Obtain Optimal Antioxidants and Health Benefits
- PMID: 38231711
- PMCID: PMC10706092
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12234281
Green Extraction of Hodgsonia heteroclita Oilseed Cake Powder to Obtain Optimal Antioxidants and Health Benefits
Abstract
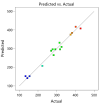
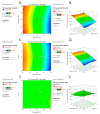
Most biowaste produced by domestic food preparation and food processing has no value, is difficult to manage, and is detrimental to the environment. Oil extraction from Hodgsonia heteroclita seeds produces large amounts of oilseed cake powder (OCP) as biowaste. The extraction of residual phytochemicals using simple and eco-friendly methods can increase the economic utility of OCP. This study optimized the extraction process for Hodgsonia heteroclita OCP using a Box-Behnken design and response surface methodology. The optimized extraction condition was 30 °C for 5 h in 50% (v/v) ethanol, giving a total phenolic content (TPC) of 414.23 mg of gallic acid equivalent/100 g dry weight (DW). Phytochemical profiles of OCP using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ECI-MS/MS) identified 4-hydroxybenzoic acid and ferulic acid as the major compounds. Antioxidant activities and enzyme inhibitory activities toward the major enzymes involved in obesity (lipase), diabetes (α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV)), Alzheimer's disease (acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), and β-secretase-1 (BACE-1)), hypertension (angiotensin-converting enzyme, ACE), and genotoxicity were also investigated. Results showed that H. heteroclita OCP possessed antioxidant activity and potential inhibitory activities against BACE-1 and ACE, while also being genome-safe. A simple extraction method for H. heteroclita OCP was developed, demonstrating the enhanced value of its phytochemical and health-promoting qualities.
Keywords: agricultural waste; enzyme inhibition; genotoxicity; phenolics; response surface methodology; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nutrients, Phytochemicals and In Vitro Disease Prevention of Nephelium hypoleucum Kurz Fruit.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 14;15(4):950. doi: 10.3390/nu15040950. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839313 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Phytochemical-Rich Citrus maxima Albedo Extract Using Response Surface Methodology.Molecules. 2023 May 16;28(10):4121. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104121. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241861 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive compounds and in vitro biological properties of Arthrospira platensis and Athrospira maxima: a comparative study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 11;14(1):23786. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74492-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39390067 Free PMC article.
-
Physico-functional properties, structural, and nutritional characterizations of Hodgsonia heteroclita oilseed cakes.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19241. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70276-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164362 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Conditions for the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Aeginetia indica L. and Its Potential Biological Applications.Molecules. 2024 Feb 28;29(5):1050. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051050. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474563 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive phytochemical profiling and biological activities of Hodgsonia heteroclita subsp. indochinensis seed extracts.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 27;10(17):e36686. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36686. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39286088 Free PMC article.
-
High Pectin Recovery from Cocoa Husks Using an Autoclave Approach: An Analysis of Its Physicochemical, Structural, and Genotoxicity Properties.Foods. 2024 Feb 22;13(5):669. doi: 10.3390/foods13050669. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38472782 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenols in Foods and Their Use in the Food Industry: Enhancing the Quality and Nutritional Value of Functional Foods.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 17;26(12):5803. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125803. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Swargiary A., Brahma D. Phytochemical Analysis and Antioxidant Activity of Hodgsonia heteroclita (Roxb) Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017;79:212–219. doi: 10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000219. - DOI
-
- Piseskul J., Suttisansanee U., Chupeerach C., Khemthong C., Thangsiri S., Temviriyanukul P., Sahasakul Y., Santivarangkna C., Chamchan R., Aursalung A., et al. Optimization of Enzyme-Assisted Mechanical Extraction Process of Hodgsonia heteroclita Oilseeds and Physical, Chemical, and Nutritional Properties of the Oils. Foods. 2023;12:292. doi: 10.3390/foods12020292. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khuntaseema B., Jomduang S. Nutritive Values of Inner Pulp from Ma-king Seed (Hodgsonia heteroclite susp. Indochinensis) Agric. Sci. J. 2014;45:725–728.
-
- Kremmyda L.S., Tvrzicka E., Stankova B., Zak A. Fatty acids as biocompounds: Their role in human metabolism, health and disease: A review. part 2: Fatty acid physiological roles and applications in human health and disease. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech Repub. 2011;155:195–218. doi: 10.5507/bp.2011.052. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

