The Improved Quality of Gluten-Free Bread Due to the Use of Flaxseed Oil Cake: A Comprehensive Study Evaluating Nutritional Value, Technological Properties, and Sensory Quality
- PMID: 38231753
- PMCID: PMC10705945
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12234320
The Improved Quality of Gluten-Free Bread Due to the Use of Flaxseed Oil Cake: A Comprehensive Study Evaluating Nutritional Value, Technological Properties, and Sensory Quality
Abstract
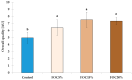
The development of gluten-free bakery products, the quality of which is comparable to the quality of regular wheat-based products, remains a technological challenge. In this study, flaxseed oil cake (FOC), a by-product of flaxseed oil extraction and a source of nutritional and functional compounds, was used as an ingredient in the experimental bread formulation as partial replacement of starches (5%, 15%, and 30%). The gluten-free breads (GFBs) were evaluated for technological parameters, nutritional value, and sensory quality. Compared with the control, all FOC-enhanced GFBs were significantly (p < 0.05) richer in proteins, fat, and dietary fibre, with an increase that was proportional to the concentration of FOC in the formulation. At low-to-moderate levels (5% and 15%), FOC improved the specific volume, texture characteristics (reduced crumb hardness, gumminess, and chewiness), and appearance of GFBs, which allowed us to ameliorate its sensory features, but at 30% of FOC, the quality of the crumb texture decreased significantly (p < 0.005). Among the experimental GFBs, FOC15% exhibited improved technological characteristics and was rated by the sensory panel as the best in terms of overall quality. The results of the conducted research highlighted the benefits of incorporating FOC into GFB as a promising approach to developing a palatable, high-quality bakery product that may be a healthier option for individuals on a gluten-free diet, offering nutritional benefits. Nevertheless, it should be emphasised that the amount of FOC in GFB requires careful regulation.
Keywords: bakery products; by-product revalorisation; gluten elimination; oilseed cake; plant-based by-products; sensory features; textural profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel Gluten-Free Bread with an Extract from Flaxseed By-Product: The Relationship between Water Replacement Level and Nutritional Value, Antioxidant Properties, and Sensory Quality.Molecules. 2022 Apr 21;27(9):2690. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092690. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566041 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Flaxseed Oil Cake Extract on the Microbial Quality, Texture and Shelf Life of Gluten-Free Bread.Foods. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):595. doi: 10.3390/foods12030595. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36766124 Free PMC article.
-
Mixture Design Applied to the Development of Chickpea-Based Gluten-Free Bread with Attractive Technological, Sensory, and Nutritional Quality.J Food Sci. 2018 Jan;83(1):188-197. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14009. Epub 2017 Dec 6. J Food Sci. 2018. PMID: 29210449
-
Plant-Based Antioxidants in Gluten-Free Bread Production: Sources, Technological and Sensory Aspects, Enhancing Strategies and Constraints.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;13(2):142. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020142. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Effects of the Different Matrices to Enhance the Polyphenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity in Gluten-Free Bread.Foods. 2023 Dec 8;12(24):4415. doi: 10.3390/foods12244415. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38137219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Malenica D., Kass M., Bhat R. Sustainable Management and Valorization of Agri-Food Industrial Wastes and By-Products as Animal Feed: For Ruminants, Non-Ruminants and as Poultry Feed. Sustainability. 2023;15:117. doi: 10.3390/su15010117. - DOI
-
- Smeu I., Dobre A.A., Cucu E.M., Mustățea G., Belc N., Ungureanu E.L. Byproducts from the Vegetable Oil Industry: The Challenges of Safety and Sustainability. Sustainability. 2022;14:2039. doi: 10.3390/su14042039. - DOI
-
- Bacenetti J., Restuccia A., Schillaci G., Failla S. Biodiesel production from unconventional oilseed crops (Linum usitatissimum L. and Camelina sativa L.) in Mediterranean conditions: Environmental sustainability assessment. Renew. Energy. 2017;112:444–456. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.05.044. - DOI
-
- Oomah B.D. Food Wastes and By-Products. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2019. Flaxseed By-products; pp. 267–289.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

