Snapshot of the Probiotic Potential of Kluveromyces marxianus DMKU-1042 Using a Comparative Probiogenomics Approach
- PMID: 38231794
- PMCID: PMC10706368
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12234329
Snapshot of the Probiotic Potential of Kluveromyces marxianus DMKU-1042 Using a Comparative Probiogenomics Approach
Abstract
Kluyveromyces marxianus is a rapidly growing thermotolerant yeast that secretes a variety of lytic enzymes, utilizes different sugars, and produces ethanol. The probiotic potential of this yeast has not been well explored. To evaluate its probiotic potential, the yeast strain Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU3-1042 was analyzed using next-generation sequencing technology. Analysis of the genomes showed that the yeast isolates had a GC content of 40.10-40.59%. The isolates had many genes related to glycerol and mannose metabolism, as well as genes for acetoin and butanediol metabolism, acetolactate synthase subunits, and lactic acid fermentation. The strain isolates were also found to possess genes for the synthesis of different vitamins and Coenzyme A. Genes related to heat and hyperosmotic shock tolerance, as well as protection against reactive oxygen species were also found. Additionally, the isolates contained genes for the synthesis of lysine, threonine, methionine, and cysteine, as well as genes with anticoagulation and anti-inflammatory properties. Based on our analysis, we concluded that the strain DMKU3-1042 possesses probiotic properties that make it suitable for use in food and feed supplementation.
Keywords: Kluyveromyces marxianus; fermentation; genes; next-generation sequencing; probiotic; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

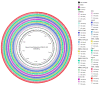
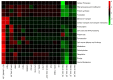



Similar articles
-
Efficient conversion of xylose to ethanol by stress-tolerant Kluyveromyces marxianus BUNL-21.Springerplus. 2016 Feb 27;5:185. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-1881-6. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27026881 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the stress responses of Kluyveromyces marxianus after an arrest during high-temperature ethanol fermentation based on integration of RNA-Seq and metabolite data.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;103(6):2715-2729. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09637-x. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30673809
-
Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus Reveals More Tolerance to Heat Shock than the Brewery Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biocontrol Sci. 2018;23(3):133-138. doi: 10.4265/bio.23.133. Biocontrol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30249963
-
Kluyveromyces marxianus as a microbial cell factory for lignocellulosic biomass valorisation.Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Nov;60:108027. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108027. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 35952960 Review.
-
Kluyveromyces marxianus: An emerging yeast cell factory for applications in food and biotechnology.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Nov 16;333:108818. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108818. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32805574 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Interactions in Food Fermentation: Interactions, Analysis Strategies, and Quality Enhancement.Foods. 2025 Jul 17;14(14):2515. doi: 10.3390/foods14142515. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40724333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Human Mycobiome: Composition, Immune Interactions, and Impact on Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 28;26(15):7281. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157281. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

