Salvia officinalis-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposites with Antibacterial Properties
- PMID: 38231963
- PMCID: PMC10708102
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15234484
Salvia officinalis-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposites with Antibacterial Properties
Abstract
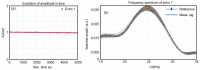
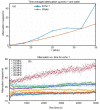
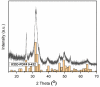
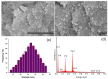
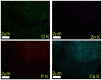
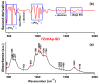
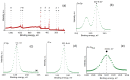
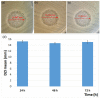
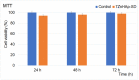
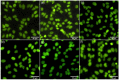
In the present study, sage-coated zinc-doped hydroxyapatite was incorporated into a dextran matrix (7ZnHAp-SD), and its physico-chemical and antimicrobial activities were investigated. A 7ZnHAp-SD nanocomposite suspension was obtained using the co-precipitation method. The stability of the nanocomposite suspension was evaluated using ultrasound measurements. The stability parameter calculated relative to double-distilled water as a reference fluid highlights the very good stability of the 7ZnHAp-SD suspension. X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiments were performed to evaluate the characteristic diffraction peak of the hydroxyapatite phase. Valuable information regarding the morphology and chemical composition of 7ZnHAp-SD was obtained via scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) studies. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) measurements were performed on the 7ZnHAp-SD suspensions in order to evaluate the functional groups present in the sample. Preliminary studies on the antimicrobial activity of 7ZnHAp-SD suspensions against the standard strains of Staphylococcus aureus 25923 ATCC, Enterococcus faecalis 29212 ATCC, Escherichia coli 25922 ATCC, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa 27853 ATCC were conducted. More than that, preliminary studies on the biocompatibility of 7ZnHAp-SD were conducted using human cervical adenocarcinoma (HeLa) cells, and their results emphasized that the 7ZnHAp-SD sample did not exhibit a toxic effect and did not induce any noticeable changes in the morphological characteristics of HeLa cells. These preliminary results showed that these nanoparticles could be possible candidates for biomedical/antimicrobial applications.
Keywords: antimicrobial applications; dextran; morphology; sage; zinc doped hydroxyapatite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest; The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Du M., Chen J., Liu K., Xing H., Song C. Recent advances in biomedical engineering of nano-hydroxyapatite including dentistry, cancer treatment and bone repair. Compos. B Eng. 2021;215:108790. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108790. - DOI
Grants and funding
- PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2019-1375/Unitatea Executiva Pentru Finantarea Invatamantului Superior a Cercetarii Dezvoltarii si Inovarii
- 331PED⁄2020/Unitatea Executiva Pentru Finantarea Invatamantului Superior a Cercetarii Dezvoltarii si Inovarii
- PC1- PN23080101/Unitatea Executiva Pentru Finantarea Invatamantului Superior a Cercetarii Dezvoltarii si Inovarii
- Contract No. T-IS 251801/04.05.2018/Scientific Research Contract
- Nr.1/4.06.2020/Scientific Research Contract
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

