Four-dimensional computational ultrasound imaging of brain hemodynamics
- PMID: 38232164
- PMCID: PMC10793943
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adk7957
Four-dimensional computational ultrasound imaging of brain hemodynamics
Abstract
Four-dimensional ultrasound imaging of complex biological systems such as the brain is technically challenging because of the spatiotemporal sampling requirements. We present computational ultrasound imaging (cUSi), an imaging method that uses complex ultrasound fields that can be generated with simple hardware and a physical wave prediction model to alleviate the sampling constraints. cUSi allows for high-resolution four-dimensional imaging of brain hemodynamics in awake and anesthetized mice.
Figures
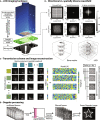
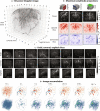
References
-
- Tanter M., Fink M., Ultrafast imaging in biomedical ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 61, 102–119 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Couade M., The advent of ultrafast ultrasound in vascular imaging: A review. J. Vasc. Diagn. Interv. 4, 9–22 (2016).
-
- Sebag F., Vaillant-Lombard J., Berbis J., Griset V., Henry J. F., Petit P., Oliver C., Shear wave elastography: A new ultrasound imaging mode for the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol. 95, 5281–5288 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Errico C., Pierre J., Pezet S., Desailly Y., Lenkei Z., Couture O., Tanter M., Ultrafast ultrasound localization microscopy for deep super-resolution vascular imaging. Nature 527, 499–502 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

