Characterization of cases and epidemiological and operational indicators of leprosy: analysis of time series and spatial distribution, Piauí state, Brazil, 2007-2021
- PMID: 38232240
- PMCID: PMC10807012
- DOI: 10.1590/S2237-96222024v33e2023090.en
Characterization of cases and epidemiological and operational indicators of leprosy: analysis of time series and spatial distribution, Piauí state, Brazil, 2007-2021
Abstract
Objective: To analyze epidemiological characteristics, temporal trends and spatial distribution of leprosy cases and indicators in the state of Piauí, 2007-2021.
Methods: This was an ecological time-series study using data from the Notifiable Health Conditions Information System, describing the spatial distribution and the temporal trend of leprosy using Prais-Winsten regression.
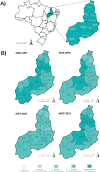
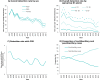
Results: A total of 17,075 new cases of leprosy were reported. There was a falling trend in the overall detection rate [annual percentage change (APC) = -6.3; 95%CI -8.1;-4.5)], detection in children under 15 years of age (APC = -8,6; 95%CI -12,7;-4,3) and detection of cases with grade 2 physical disability (APC = -4,4; 95%CI -7,0;-1,8). There was a rising trend in the proportion of multibacillary cases. Spatial distribution of the average detection rate identified hyperendemic areas in the Carnaubais, Entre Rios, Vale dos Rios Piauí e Itaueiras regions.
Conclusion: High leprosy detection rates were found, despite the falling trend of indicators, except the proportion of multibacillary cases.
Main results: Between 2007 and 2021, Piauí showed an improving trend in all indicators analyzed, except the proportion of new multibacillary cases. Spatial distribution identified hyperendemic areas in different regions of the state.
Implications for services: This study provides health services with a broad overview of the epidemiological situation of leprosy in Piauí, with evidence of the populations and locations most affected by the disease, whereby public authorities need to reinforce the promotion of health actions.
Perspectives: It is expected that actions to prevent and control the disease will be adopted, such as offering early diagnosis, ensuring correct treatment and implementing measures to prevent physical disabilities.
Objetivo: Analizar características epidemiológicas, tendencias temporales, distribución espacial de casos y indicadores de lepra en el estado de Piauí, 2007-2021.
Métodos: Estudio ecológico de series temporales con datos del Sistema de Información de Enfermedades de Notificación que describen la distribución espacial y la tendencia temporal de la lepra mediante la regresión de Prais-Winsten.
Resultados: Se notificaron 17.075 nuevos casos de lepra. Hubo tendencia decreciente en las tasas de detección general [variación porcentual anual (VPA) = -6,3; IC95% -8,1; -4,5], detección en menores de 15 años (VPA = -8,6; IC95% -12,7; -4,3), y detección de casos con discapacidad física grado 2 (VPA = -4,4; IC95%-7,0; -1,8). Hubo una tendencia creciente en la proporción de casos multibacilares. La distribución espacial de la tasa promedio de detección identificó áreas hiperendémicas en las regiones de Carnaubais, Entre Rios, Vale dos Rios Piauí y Itaueiras.
Conclusión: Se observaron altas tasas de detección de lepra, a pesar de la tendencia decreciente de los indicadores, excepto la proporción de casos multibacilares
Objetivo: Analisar características epidemiológicas, tendência temporal, distribuição espacial de casos e indicadores da hanseníase no estado do Piauí, 2007-2021.
Métodos: Estudo ecológico de séries temporais com dados do Sistema de Informação de Agravos de Notificação, descrevendo a distribuição espacial e a tendência temporal da hanseníase pela regressão de Prais-Winsten.
Resultados: Foram notificados 17.075 novos casos de hanseníase. A distribuição espacial da taxa média de detecção identificou áreas hiperendêmicas nas regiões Carnaubais, Entre Rios, Vale dos Rios Piauí e Itaueiras. Verificou-se tendência decrescente nas taxas de detecção geral [variação percentual anual (VPA) = -6,3; IC95% -8,1;-4,5], de detecção em menores de 15 anos (VPA = -8,6; IC95%12,7;-4,3) e de detecção de casos com grau 2 de incapacidade física (VPA = -4,4; IC95%-7,0;1,8), e tendência crescente na proporção de casos multibacilares.
Conclusão: Observaram-se elevadas taxas de detecção de hanseníase, apesar da tendência decrescente dos indicadores, exceto a proporção de casos multibacilares.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Magnitude and temporal trend of leprosy indicators in Goiás, Brazil: an ecological study 2001-2017.Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2020 Nov 6;29(5):e2019575. doi: 10.1590/S1679-49742020000500012. eCollection 2020. Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2020. PMID: 33175008 English, Portuguese.
-
Clinical-epidemiological characteristics and temporal trend of new cases of grade 2 disability leprosy in the state of Maranhão, Brazil, 2011- 2020.Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2023 Sep 18;32(2):e2022435. doi: 10.1590/S2237-96222023000200026. eCollection 2023. Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2023. PMID: 37729263 Free PMC article.
-
Trend of leprosy in individuals under the age of 15 in Mato Grosso (Brazil), 2001-2013.Rev Saude Publica. 2017 Apr 10;51:28. doi: 10.1590/S1518-8787.2017051006884. Rev Saude Publica. 2017. PMID: 28423139 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial distribution of leprosy in Brazil: a literature review.Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017 Jul-Aug;50(4):439-449. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0170-2016. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017. PMID: 28954063 Review.
-
Epidemiological situation of leprosy in Salvador from 2001 to 2009.An Bras Dermatol. 2014 Jan-Feb;89(1):107-17. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142175. An Bras Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24626655 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strengthening epidemiological surveillance in primary healthcare to combat Hansen's disease: reflections on the disease in the Brazilian context, 2025.Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2025 Aug 4;34:e20240019. doi: 10.1590/S2237-96222025v34e20240019.en. Epidemiol Serv Saude. 2025. PMID: 40767698 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of healthcare services to reduce leprosy in Brazil: a trend analysis from 2001 to 2020.Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2024 Jul 1;27:e240034. doi: 10.1590/1980-549720240034. eCollection 2024. Rev Bras Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38958370 Free PMC article.
-
Global Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence and Disability-Adjusted Life Years of Leprosy from 1990 to 2019: An Age-Period-Cohort Analysis Using the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025 Apr 9;18:883-898. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S508600. eCollection 2025. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40225309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global leprosy (Hansen disease) update, 2021: moving towards interruption of transmission. 2021. [citado em 5 de maio de 2023]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/who-wer9736-429-450 .
-
- Ministério da Saúde (BR) Datasus: Tabnet - informações de saúde, epidemiológicas e morbidade. 2022. [citado em 29 de março de 2022]. http://www2.datasus.gov.br/DATASUS/index.php?%20area=0203.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

