Lymph node and tumor-associated PD-L1+ macrophages antagonize dendritic cell vaccines by suppressing CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 38232703
- PMCID: PMC10829875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101377
Lymph node and tumor-associated PD-L1+ macrophages antagonize dendritic cell vaccines by suppressing CD8+ T cells
Abstract
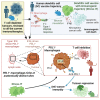
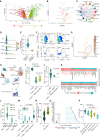
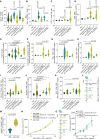
Current immunotherapies provide limited benefits against T cell-depleted tumors, calling for therapeutic innovation. Using multi-omics integration of cancer patient data, we predict a type I interferon (IFN) responseHIGH state of dendritic cell (DC) vaccines, with efficacious clinical impact. However, preclinical DC vaccines recapitulating this state by combining immunogenic cancer cell death with induction of type I IFN responses fail to regress mouse tumors lacking T cell infiltrates. Here, in lymph nodes (LNs), instead of activating CD4+/CD8+ T cells, DCs stimulate immunosuppressive programmed death-ligand 1-positive (PD-L1+) LN-associated macrophages (LAMs). Moreover, DC vaccines also stimulate PD-L1+ tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). This creates two anatomically distinct niches of PD-L1+ macrophages that suppress CD8+ T cells. Accordingly, a combination of PD-L1 blockade with DC vaccines achieves significant tumor regression by depleting PD-L1+ macrophages, suppressing myeloid inflammation, and de-inhibiting effector/stem-like memory T cells. Importantly, clinical DC vaccines also potentiate T cell-suppressive PD-L1+ TAMs in glioblastoma patients. We propose that a multimodal immunotherapy and vaccination regimen is mandatory to overcome T cell-depleted tumors.
Keywords: DAMPs; ICB; NF-κB; PD-1; TAAs; apoptosis; damage-associated molecular patterns; immune-checkpoint blockers; mature regulatory DCs; mregDC; necroptosis; nuclear factor κB; programmed cell death-1; single-cell omics; tumor-associated antigens.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.D.G. received honoraria/funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Miltenyi Biotec, Novigenix, SOTIO, and IsoPlexis.
Figures





References
-
- Sharma P., Allison J.P. Dissecting the mechanisms of immune checkpoint therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020;20:75–76. - PubMed
-
- Naulaerts S., Datsi A., Borras D.M., Antoranz Martinez A., Messiaen J., Vanmeerbeek I., Sprooten J., Laureano R.S., Govaerts J., Panovska D., et al. Multiomics and spatial mapping characterizes human CD8+ T cell states in cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023;15 - PubMed
-
- Borras D.M., Verbandt S., Ausserhofer M., Sturm G., Lim J., Laureano R.S., Vanmeerbeek I., Sprooten J., Hong Y., Wall R., et al. Single cell dynamics of tumour specificity vs. bystander activity in CD8+T cells define the diverse immune landscapes in colorectal cancer. Cell Discov. 2023;9 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

