Role of Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 in Inflammation and Pathogen-Associated Interactions
- PMID: 38232720
- PMCID: PMC10866614
- DOI: 10.1159/000535793
Role of Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 in Inflammation and Pathogen-Associated Interactions
Abstract
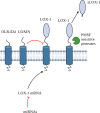
Background: Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) is known as a major receptor for oxidized low-density lipoproteins (oxLDL) and plays a significant role in the genesis of atherosclerosis. Recent research has shown its involvement in cancer, ischemic stroke, and diabetes. LOX-1 is a C-type lectin receptor and is involved in the activation of immune cells and inflammatory processes. It may further interact with pathogens, suggesting a role in infections or the host's response.
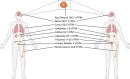
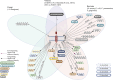
Summary: This review compiles the current knowledge of potential implications of LOX-1 in inflammatory processes and in host-pathogen interactions with a particular emphasis on its regulatory role in immune responses. Also discussed are genomic and structural variations found in LOX-1 homologs across different species as well as potential involvements of LOX-1 in inflammatory processes from the angle of different cell types and organ-specific interactions.
Key messages: The results presented reveal both similar and different structures in human and murine LOX-1 and provide clues as to the possible origins of different modes of interaction. These descriptions raise concerns about the suitability, particularly of mouse models, that are often used in the analysis of its functionality in humans. Further research should also aim to better understand the mostly unknown binding and interaction mechanisms between LOX-1 and different pathogens. This pursuit will not only enhance our understanding of LOX-1 involvement in inflammatory processes but also identify potential targets for immunomodulatory approaches.
Keywords: C-type lectin-like receptors; Infection response; Inflammation; LOX-1; Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1; Oxidized low-density lipoprotein.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 (LOX-1): A Potential Therapeutic Target in Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Aug;16(4):1412-1423. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01307-z. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39576412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Oxidized LDL receptors: a recent update.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2023 Aug 1;34(4):147-155. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000884. Epub 2023 May 4. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2023. PMID: 37171285 Review.
-
PPP2CB aggravates atherosclerosis-related dyslipidemia via LOX-1/MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jul 3;24(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02647-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40611318 Free PMC article.
-
Innate extracellular mouse Hsp70 inflammatory properties are mediated by the interaction of Siglec-E and LOX-1 receptors.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2025 Jul;30(4):100083. doi: 10.1016/j.cstres.2025.100083. Epub 2025 May 22. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2025. PMID: 40412547 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1 (LOX-1): A Potential Therapeutic Target in Ischemic Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Aug;16(4):1412-1423. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01307-z. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 39576412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 by Porphyromonas gingivalis promoting progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-/- mice.J Dent Sci. 2025 Apr;20(2):754-763. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.10.015. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Dent Sci. 2025. PMID: 40224117 Free PMC article.
-
A Review: Can Cytokines Induce Vascular Inflammation as a Sequela of Viral Infections?Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 21;8(7):e71105. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71105. eCollection 2025 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40692575 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Uptake of Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein by Macrophages Using Multiple Aptamer Combinations.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jan 20;8(1):457-474. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c01432. Epub 2025 Jan 6. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 39762152 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Aptamer Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Reducing Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Internalization by Macrophages.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Jul 16;17(28):40101-40115. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c07018. Epub 2025 Jul 1. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40591889 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

