Using electronic health records to enhance surveillance of diabetes in children, adolescents and young adults: a study protocol for the DiCAYA Network
- PMID: 38233060
- PMCID: PMC10806714
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073791
Using electronic health records to enhance surveillance of diabetes in children, adolescents and young adults: a study protocol for the DiCAYA Network
Abstract
Introduction: Traditional survey-based surveillance is costly, limited in its ability to distinguish diabetes types and time-consuming, resulting in reporting delays. The Diabetes in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults (DiCAYA) Network seeks to advance diabetes surveillance efforts in youth and young adults through the use of large-volume electronic health record (EHR) data. The network has two primary aims, namely: (1) to refine and validate EHR-based computable phenotype algorithms for accurate identification of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youth and young adults and (2) to estimate the incidence and prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youth and young adults and trends therein. The network aims to augment diabetes surveillance capacity in the USA and assess performance of EHR-based surveillance. This paper describes the DiCAYA Network and how these aims will be achieved.
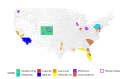
Methods and analysis: The DiCAYA Network is spread across eight geographically diverse US-based centres and a coordinating centre. Three centres conduct diabetes surveillance in youth aged 0-17 years only (component A), three centres conduct surveillance in young adults aged 18-44 years only (component B) and two centres conduct surveillance in components A and B. The network will assess the validity of computable phenotype definitions to determine diabetes status and type based on sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of the phenotypes against the gold standard of manually abstracted medical charts. Prevalence and incidence rates will be presented as unadjusted estimates and as race/ethnicity, sex and age-adjusted estimates using Poisson regression.
Ethics and dissemination: The DiCAYA Network is well positioned to advance diabetes surveillance methods. The network will disseminate EHR-based surveillance methodology that can be broadly adopted and will report diabetes prevalence and incidence for key demographic subgroups of youth and young adults in a large set of regions across the USA.
Keywords: adolescent; diabetes & endocrinology; epidemiology; health informatics; paediatric endocrinology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Steinmetz JD, Bourne RRA, Briant PS. Blindness and vision impairment collaborators, study Vlegotgbod. causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of Avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: the right to sight: an analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet Glob Health 2021;9:e144–60. 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30489-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Diabetes Statistics Report; 2020 Secondary National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020. 2022. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/diabetes-stat-report.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U18 DP006510/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006510/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18DP006518/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP006694/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- P30 DK097512/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK111022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP006509/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006506/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006518/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006512/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP006500/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006517/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006506/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18DP006521/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- P30 DK111024/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U18DP006517/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP006512/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006521/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006500/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP006693/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006513/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP006513/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical