High-content screening identifies a small molecule that restores AP-4-dependent protein trafficking in neuronal models of AP-4-associated hereditary spastic paraplegia
- PMID: 38233389
- PMCID: PMC10794252
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44264-1
High-content screening identifies a small molecule that restores AP-4-dependent protein trafficking in neuronal models of AP-4-associated hereditary spastic paraplegia
Abstract
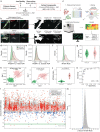
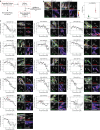
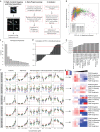
Unbiased phenotypic screens in patient-relevant disease models offer the potential to detect therapeutic targets for rare diseases. In this study, we developed a high-throughput screening assay to identify molecules that correct aberrant protein trafficking in adapter protein complex 4 (AP-4) deficiency, a rare but prototypical form of childhood-onset hereditary spastic paraplegia characterized by mislocalization of the autophagy protein ATG9A. Using high-content microscopy and an automated image analysis pipeline, we screened a diversity library of 28,864 small molecules and identified a lead compound, BCH-HSP-C01, that restored ATG9A pathology in multiple disease models, including patient-derived fibroblasts and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons. We used multiparametric orthogonal strategies and integrated transcriptomic and proteomic approaches to delineate potential mechanisms of action of BCH-HSP-C01. Our results define molecular regulators of intracellular ATG9A trafficking and characterize a lead compound for the treatment of AP-4 deficiency, providing important proof-of-concept data for future studies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by a joint research agreement between Boston Children’s Hospital and Mitobridge Inc., now owned by Astellas Pharmaceuticals Inc. D.E.F. has served as a consultant to Health Advances LLC, has received speaker honoraria from the Movement Disorders Society and publishing royalties from Cambridge University Press. M.Sa. reports grant support from Novartis, Biogen, Astellas, Aeovian, Bridgebio, and Aucta unrelated to this project. He has served on Scientific Advisory Boards for Novartis, Roche, Regenxbio, SpringWorks Therapeutics, Jaguar Therapeutics, and Alkermes. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Update of
-
High-Content Small Molecule Screen Identifies a Novel Compound That Restores AP-4-Dependent Protein Trafficking in Neuronal Models of AP-4-Associated Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 12:rs.3.rs-3036166. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3036166/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 17;15(1):584. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44264-1. PMID: 37398196 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

