BACH2-mediated CD28 and CD40LG axes contribute to pathogenesis and progression of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 38233409
- PMCID: PMC10794190
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06453-8
BACH2-mediated CD28 and CD40LG axes contribute to pathogenesis and progression of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
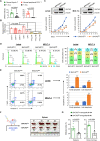
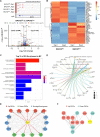
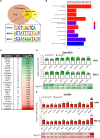
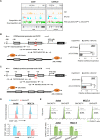
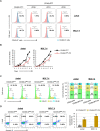
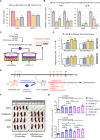
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive subtype of ALL characterized by its high heterogeneity and unfavorable clinical features. Despite improved insights in genetic and epigenetic landscapes of T-ALL, the molecular mechanisms that drive malignant T-cell development remain unclear. BTB and CNC homology 2 (BACH2) is a lymphoid-specific transcription repressor recognized as a tumor suppressor in B-cell malignancies, but little is known about its function and regulatory network in T-ALL. Here we found extremely low levels of BACH2 in T-ALL clinical samples and cell lines compared to normal T cells. Overexpression of BACH2 in T-ALL cells not only induced cell growth retardation but also inhibited cancer progression and infiltration in xenografts. Further RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis revealed significant alterations in regulation of defense and immune responses in T-ALL cells upon BACH2 overexpression. Strikingly, CD28 and CD40LG, two essential stimulatory molecules on T cells, were for the first time identified as novel downstream targets repressed by BACH2 in T-ALL cells. Interestingly, both CD28 and CD40LG were indispensable for T-ALL survival, since largely or completely silencing CD28 and CD40LG led to rapid cell death, whereas partial knockdown of them resulted in cell-cycle arrest and enhanced apoptosis. More importantly, BACH2-mediated CD28 and CD40LG signals contributed to cell migration and dissemination of T-ALL cells to the bone marrow, thus adding a new layer to the BACH2-mediated tumor immunoregulation in T-cell malignancies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BACH2-mediated FOS confers cytarabine resistance via stromal microenvironment alterations in pediatric ALL.Cancer Sci. 2021 Mar;112(3):1235-1250. doi: 10.1111/cas.14792. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33393145 Free PMC article.
-
Ikaros regulation of the BCL6/BACH2 axis and its clinical relevance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):8022-8034. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14038. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28030830 Free PMC article.
-
Bach2 in CD4+ T cells from SLE patients modulates B-cell differentiation and IgG production.Eur J Immunol. 2023 Apr;53(4):e2250109. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250109. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Eur J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36781170
-
The Bach Family of Transcription Factors: A Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Jun;50(3):345-56. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8538-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27052415 Review.
-
BTB domain and CNC homolog 2: A master regulator that controls immune response and cancer progression.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Jul;1880(3):189325. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2025.189325. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40252853 Review.
Cited by
-
The causal relationship between circulating inflammatory proteins, gut microbiotas, immune cells and leukemia: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 19;16(1):1157. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02863-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40537729 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immune-related biomarkers for glaucoma using gene expression profiling.Front Genet. 2024 Apr 17;15:1366453. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1366453. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38694874 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

