Genome-wide association identifies novel ROP risk loci in a multiethnic cohort
- PMID: 38233474
- PMCID: PMC10794688
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-05743-9
Genome-wide association identifies novel ROP risk loci in a multiethnic cohort
Abstract
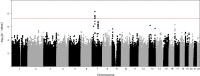
We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in a multiethnic cohort of 920 at-risk infants for retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), a major cause of childhood blindness, identifying 1 locus at genome-wide significance level (p < 5×10-8) and 9 with significance of p < 5×10-6 for ROP ≥ stage 3. The most significant locus, rs2058019, reached genome-wide significance within the full multiethnic cohort (p = 4.96×10-9); Hispanic and European Ancestry infants driving the association. The lead single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) falls in an intronic region within the Glioma-associated oncogene family zinc finger 3 (GLI3) gene. Relevance for GLI3 and other top-associated genes to human ocular disease was substantiated through in-silico extension analyses, genetic risk score analysis and expression profiling in human donor eye tissues. Thus, we identify a novel locus at GLI3 with relevance to retinal biology, supporting genetic susceptibilities for ROP risk with possible variability by race and ethnicity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.C. receives research support from Genentech (San Francisco, CA). J.P.C. was a consultant to Boston AI Lab (Boston, MA). R.V.P.C. is on the Scientific Advisory Board for Phoenix Technology Group (Pleasanton, CA), a consultant for Alcon (Ft Worth, TX). M.F.C. was previously a consultant for Novartis (Basel, Switzerland), and was previously an equity owner of InTeleretina, LLC (Honolulu, HI). J.P.C. and R.V.P.C. are equity owners of Siloam Vision. M.M.D. receives research grant support from Genentech (San Francisco, CA). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Genome-wide association identifies novel ROP risk loci in a multi-ethnic cohort.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 May 16:rs.3.rs-2855404. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2855404/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Commun Biol. 2024 Jan 17;7(1):107. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05743-9. PMID: 37292936 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.

