Safety and Effectiveness of Molnupiravir in Japanese Patients with COVID-19: Final Report of Post-marketing Surveillance in Japan
- PMID: 38233606
- PMCID: PMC10828263
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-023-00915-w
Safety and Effectiveness of Molnupiravir in Japanese Patients with COVID-19: Final Report of Post-marketing Surveillance in Japan
Abstract
Introduction: Molnupiravir is an orally available prodrug of N-hydroxycytidine that received special approval for emergency treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Japan in December 2021 and full approval in April 2023. To assess the real-world safety and effectiveness of molnupiravir in Japanese patients with COVID-19, we conducted nationwide post-marketing surveillance to collect data at registered institutions in Japan.
Methods: The surveillance data were collected from December 27, 2021, to May 2, 2023. All reported adverse events were collected for safety analysis. Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were assessed by the treating physicians. Effectiveness was assessed by the composite of hospitalization or all-cause death in outpatients and the composite of oxygen/mechanical ventilation initiation or all-cause death in inpatients. The observation period was from molnupiravir initiation through day 29.
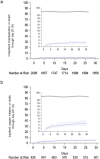
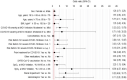
Results: Of 3214 patients enrolled in the survey, 3179 were analyzed for safety. At baseline, 52.31% (1663/3179) of patients were male, the median (range) age was 69.0 (18-107) years, 82.38% (2619/3179) received COVID-19 vaccines, and 95.72% (3043/3179) had risk factors for severe COVID-19 illness. COVID-19 severity at baseline was mild in 86.44% (2748/3179) and moderate I in 10.22% (325/3179). A total of 205 ADRs occurred in 5.50% (175/3179) of patients; ADRs that occurred in > 0.5% of patients were diarrhea (1.86% [59/3179]) and rash (0.69% [22/3179]). Seven serious ADRs were reported in seven patients. In the effectiveness analysis population, the incidence of all-cause death through day 29 was 1.14% (34/2988), and the incidence of death through day 29 related to COVID-19 was 0.40% (12/2988). The cumulative incidence of the composite endpoint was 2.34% (47/2006) in outpatients and 4.60% (38/826) in inpatients.
Conclusions: This large-scale survey showed that molnupiravir was safe and effective in real-world settings in highly vaccinated Japanese patients with COVID-19, including older patients and those with comorbidities.
Keywords: COVID-19; Effectiveness; Japan; Molnupiravir; Post-marketing surveillance; Safety.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Shohei Shinozaki, Asuka Watanabe, Masahiro Kimata, Makoto Miyazaki and Shinichiroh Maekawa are all employees of MSD K.K.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Molnupiravir (LAGEVRIO®) Capsules in Japanese Patients with COVID-19: Interim Report of Post-marketing Surveillance in Japan.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 Apr;12(4):1119-1136. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00782-5. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 36928787 Free PMC article.
-
The Durable Safety and Effectiveness of Lixisenatide in Japanese People with Type 2 Diabetes: The Post-Marketing Surveillance PRANDIAL Study.Adv Ther. 2022 Jun;39(6):2873-2888. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02121-5. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35449321 Free PMC article.
-
Ensitrelvir for the treatment of COVID-19: Final analysis of a post-marketing surveillance from Japan.J Infect Chemother. 2025 Mar;31(3):102574. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2024.12.003. Epub 2024 Dec 3. J Infect Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39631674
-
Molnupiravir Use Among Patients with COVID-19 in Real-World Settings: A Systematic Literature Review.Infect Dis Ther. 2024 Jun;13(6):1177-1198. doi: 10.1007/s40121-024-00976-5. Epub 2024 May 14. Infect Dis Ther. 2024. PMID: 38743192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of molnupiravir for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023 Jul 5;78(7):1586-1598. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad132. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37170886 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of pharmacokinetics and tolerability following single-dose administration of molnupiravir in participants with hepatic or renal impairment.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Dec;17(12):e70073. doi: 10.1111/cts.70073. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39601078 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient-Reported Adverse Events Among Elderly Patients Receiving Novel Oral COVID-19 Antivirals: A Nationwide Sampled Survey in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2024 Oct 28;39(41):e270. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e270. J Korean Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39468947 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Molnupiravir to Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 in Immunocompromised Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 5;16(5):1055. doi: 10.3390/cancers16051055. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473412 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Molnupiravir Versus Best Supportive Care for the Treatment of Outpatient COVID-19 in High-Risk Older Adults in Japan.Pharmacoecon Open. 2025 Jul;9(4):571-584. doi: 10.1007/s41669-025-00578-y. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Pharmacoecon Open. 2025. PMID: 40266489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Press briefing on WHO Mission to China and novel coronavirus outbreak. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/press-briefing-on-w.... Accessed 10 Jun 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

