Safety and effectiveness of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging-guided laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatic tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38234399
- PMCID: PMC10791760
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1309593
Safety and effectiveness of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging-guided laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatic tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Previous clinical investigations have reported inconsistent findings regarding the feasibility of utilizing indocyanine green fluorescence imaging (ICGFI) in laparoscopic liver tumor removal. This meta-analysis aims to comprehensively evaluate the safety and effectiveness of ICGFI in laparoscopic hepatectomy (LH).
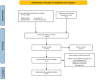
Methods: A systematic search of pertinent clinical studies published before January 30th, 2023 was conducted in databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and Web of Science. The search strategy encompassed key terms such as "indocyanine green fluorescence," "ICG fluorescence," "laparoscopic hepatectomy," "hepatectomies," "liver Neoplasms," "hepatic cancer," and "liver tumor." Additionally, we scrutinized the reference lists of included articles to identify supplementary studies. we assessed the quality of the incorporated studies and extracted clinical data. Meta-analysis was performed using STATA v.17.0 software. Either a fixed-effects or a random-effects model was employed to compute combined effect sizes, accompanied by 95% confidence intervals (CIs), based on varying levels of heterogeneity.
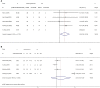
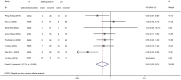
Results: This meta-analysis encompassed eleven retrospective cohort studies, involving 959 patients in total. Our findings revealed that, in comparison to conventional laparoscopic hepatectomy, patients receiving ICGFI-guided LH exhibited a higher R0 resection rate (OR: 3.96, 95% CI: 1.28, 12.25, I2 = 0.00%, P = 0.778) and a diminished incidence of intraoperative blood transfusion (OR: 0.42, 95% CI: 0.22, 0.81, I 2 = 51.1%, P = 0.056). Additionally, they experienced shorter postoperative hospital stays (WMD: -1.07, 95% CI: -2.00, -0.14, I 2 = 85.1%, P = 0.000). No statistically significant differences emerged between patients receiving ICGFI-guided LH vs. those undergoing conventional LH in terms of minimal margin width and postoperative complications.
Conclusion: ICGFI-guided LH demonstrates marked superiority over conventional laparoscopic liver tumor resection in achieving R0 resection and reducing intraoperative blood transfusion rates. This technique appears to hold substantial promise. Nonetheless, further studies are needed to explore potential long-term benefits associated with patients undergoing ICGFI-guided LH.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD 42023398195.
Keywords: fluorescence imaging; indocyanine green; laparoscopic hepatectomy; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Zhou, Du, Liu, Dong, Ma, Sun and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources