This is a preprint.
Magnetoelectric Nanodiscs Enable Wireless Transgene-Free Neuromodulation
- PMID: 38234742
- PMCID: PMC10793401
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.24.573272
Magnetoelectric Nanodiscs Enable Wireless Transgene-Free Neuromodulation
Update in
-
Magnetoelectric nanodiscs enable wireless transgene-free neuromodulation.Nat Nanotechnol. 2025 Jan;20(1):121-131. doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01798-9. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Nat Nanotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39394431 Free PMC article.
Abstract
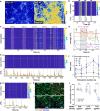
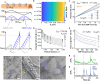
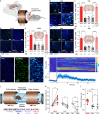
Deep-brain stimulation (DBS) with implanted electrodes revolutionized treatment of movement disorders and empowered neuroscience studies. Identifying less invasive alternatives to DBS may further extend its clinical and research applications. Nanomaterial-mediated transduction of magnetic fields into electric potentials offers an alternative to invasive DBS. Here, we synthesize magnetoelectric nanodiscs (MENDs) with a core-double shell Fe3O4-CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 architecture with efficient magnetoelectric coupling. We find robust responses to magnetic field stimulation in neurons decorated with MENDs at a density of 1 μg/mm2 despite individual-particle potentials below the neuronal excitation threshold. We propose a model for repetitive subthreshold depolarization, which combined with cable theory, corroborates our findings in vitro and informs magnetoelectric stimulation in vivo. MENDs injected into the ventral tegmental area of genetically intact mice at concentrations of 1 mg/mL enable remote control of reward behavior, setting the stage for mechanistic optimization of magnetoelectric neuromodulation and inspiring its future applications in fundamental and translational neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Y.J.K., F.K. and P.A. have applied for a provisional US patent related to the magnetoelectric nanodisc technology reported in the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Aum D. J. & Tierney T. S. Deep brain stimulation: foundations and future trends. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark 23, 162–182 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Klomjai W., Katz R. & Lackmy-Vallée A. Basic principles of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and repetitive TMS (rTMS). Annals of physical and rehabilitation medicine 58, 208–213 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Hallett M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and the human brain. Nature 406, 147–150 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi M. & Pascual-Leone A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology. The Lancet Neurology 2, 145–156 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
