This is a preprint.
PDGFRα/β heterodimer activation negatively affects downstream ERK1/2 signaling and cellular proliferation
- PMID: 38234806
- PMCID: PMC10793460
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.27.573428
PDGFRα/β heterodimer activation negatively affects downstream ERK1/2 signaling and cellular proliferation
Update in
-
PDGFRα/β heterodimer activation negatively affects downstream ERK1/2 signaling and cellular proliferation.Nat Commun. 2025 May 22;16(1):4754. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59938-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40404618 Free PMC article.
Abstract
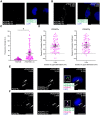
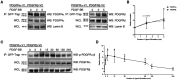
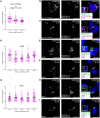
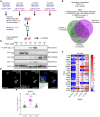
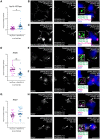
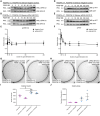
The platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) family of receptor tyrosine kinases allows cells to communicate with one another by binding to growth factors at the plasma membrane and activating intracellular signaling pathways to elicit responses such as migration, proliferation, survival and differentiation. The PDGFR family consists of two receptors, PDGFRα and PDGFRβ, that dimerize to form PDGFRα homodimers, PDGFRα/β heterodimers and PDGFRβ homodimers. Here, we overcame prior technical limitations in visualizing and purifying PDGFRα/β heterodimers by generating a cell line stably expressing C-terminal fusions of PDGFRα and PDGFRβ with bimolecular fluorescence complementation fragments corresponding to the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the Venus fluorescent protein, respectively. We found that these receptors heterodimerize relatively quickly in response to PDGF-BB ligand treatment, with a peak of receptor autophosphorylation following 5 minutes of ligand stimulation. Moreover, we demonstrated that PDGFRα/β heterodimers are rapidly internalized into early endosomes, particularly signaling endosomes, where they dwell for extended lengths of time. We showed that PDGFRα/β heterodimer activation does not induce downstream phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and significantly inhibits cell proliferation. Further, we characterized the PDGFR dimer-specific interactome and identified MYO1D as a novel protein that preferentially binds PDGFRα/β heterodimers. We demonstrated that knockdown of MYO1D leads to retention of PDGFRα/β heterodimers at the plasma membrane, resulting in increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and increased cell proliferation. Collectively, our findings impart valuable insight into the molecular mechanisms by which specificity is introduced downstream of PDGFR activation to differentially propagate signaling and generate distinct cellular responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol Rev 79, 1283–1316 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Hoch R. V., Soriano P., Roles of PDGF in animal development. Development 130, 4769–4784 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Williams L. T., Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science 243, 1564–1570 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Matsui T. et al., Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science 243, 800–804 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Seifert R. A. et al., Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 264, 8771–8778 (1989). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
