This is a preprint.
Immune-responsive gene-1: The mitochondrial Key to Th17 Cell Pathogenicity in CNS Autoimmunity
- PMID: 38234838
- PMCID: PMC10793427
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.12.24.573264
Immune-responsive gene-1: The mitochondrial Key to Th17 Cell Pathogenicity in CNS Autoimmunity
Update in
-
Immune-responsive gene 1: The mitochondrial key to Th17 cell pathogenicity in CNS autoimmunity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Aug 12;122(32):e2427052122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2427052122. Epub 2025 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40758870
Abstract
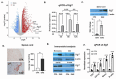
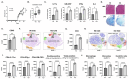
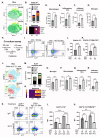
Pathogenic Th17 cells play crucial roles in CNS autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), but their regulation by endogenous mechanisms remains unknown. Through RNA-seq analysis of primary brain glial cells, we identified immuno-responsive gene 1 (Irg1) as one of the highly upregulated gene under inflammatory conditions. Validation in the spinal cord of animals with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an MS model, confirmed elevated Irg1 levels in myeloid, CD4, and B cells in the EAE group raising the concern if Irg1 is detrimental or protective. Irg1 knockout (KO) mice exhibited severe EAE disease, increased mononuclear cell infiltration, and increased levels of triple-positive CD4+ T cells expressing IL17a, GM-CSF, and IFNγ. A lack of Irg1 in macrophages elevates Class II expression, promoting the polarization of myelin-primed CD4+ T cells into pathogenic Th17 cells via the NLRP3/IL-1β axis. Adoptive transfer in Rag-1 KO and single-cell RNA sequencing highlighted the crucial role of Irg1 in shaping pathogenic Th17 cells. Moreover, bone marrow chimeras revealed that immune cells lacking Irg1 maintained pathogenic and inflammatory phenotypes, suggesting its protective role in autoimmune diseases, including MS.
Keywords: EAE; GM-CSF; IFNγ; IL17a; IL1β; Irg1; Multiple sclerosis; Th17; macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Almolda B., Gonzalez B., and Castellano B.. 2011. Antigen presentation in EAE: role of microglia, macrophages and dendritic cells. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 16: 1157–1171. - PubMed
-
- Moser T., Akgun K., Proschmann U., Sellner J., and Ziemssen T.. 2020. The role of TH17 cells in multiple sclerosis: Therapeutic implications. Autoimmun Rev 19: 102647. - PubMed
-
- Bomfim C. C. B., Fisher L., Amaral E. P., Mittereder L., McCann K., Correa A. A. S., Namasivayam S., Swamydas M., Moayeri M., Weiss J. M., Chari R., McVicar D. W., Costa D. L., D’Imperio Lima M. R., and Sher A.. 2022. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Induces Irg1 in Murine Macrophages by a Pathway Involving Both TLR-2 and STING/IFNAR Signaling and Requiring Bacterial Phagocytosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12: 862582. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
