New-Onset Psoriatic Arthritis Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in a Psoriatic Patient Under Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Biologic Treatment: What Now?
- PMID: 38234927
- PMCID: PMC10793470
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.50723
New-Onset Psoriatic Arthritis Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in a Psoriatic Patient Under Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Biologic Treatment: What Now?
Abstract
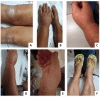
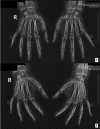
During the COVID-19 pandemic, anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were quickly developed and administered to the population worldwide. As is expected with new vaccine products, adverse reactions following immunization have been reported, namely, the development and/or exacerbation of autoimmune/autoinflammatory diseases, including rheumatic diseases. Here, we report a clinical case of a 56-year-old woman with a 44-year history of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis under treatment with an anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha biosimilar (adalimumab) with good control of skin disease and without rheumatic involvement to date who came to us with complaints of migratory polyarthralgia starting one week after receiving the second dose of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. The condition progressed over the following months and a diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis was established. Biologic treatment was switched to an anti-interleukin 17A (secukinumab), with a very good clinical cutaneous and articular response, which was sustained up to the present moment. The mechanisms behind the exacerbation or new-onset of autoimmune/autoinflammatory diseases after receiving anti-COVID-19 vaccines are not yet fully understood, requiring further investigation. It is also not known whether rheumatic symptoms post-COVID-19 infection will have similar mechanisms to rheumatic symptoms post-anti-COVID-19 vaccination. With the continuing worldwide vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, clinicians need to be prepared to discuss the risks and benefits of vaccination and should be aware that it may cause or exacerbate immune disorders such as psoriatic arthritis, warranting close follow-up in terms of disease progression and treatment.
Keywords: autoimmune disease flare; biologic treatment; covid-19 vaccination; mrna vaccine; psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis; reactive arthritis.
Copyright © 2023, Sousa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Baseline factors associated with self-reported disease flares following COVID-19 vaccination among adults with systemic rheumatic disease: results from the COVID-19 global rheumatology alliance vaccine survey. Rider LG, Parks CG, Wilkerson J, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022;61:0–50. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
