Embelin: A multifaceted anticancer agent with translational potential in targeting tumor progression and metastasis
- PMID: 38234968
- PMCID: PMC10792175
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2023-6590
Embelin: A multifaceted anticancer agent with translational potential in targeting tumor progression and metastasis
Abstract
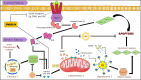
Embelin, a natural para-benzoquinone product, is derived from plants of the Embelia genus, particularly Embelia ribes Burm.f. A staple in traditional medicinal formulations for centuries, Embelin's pharmacological actions are attributed to the hydroxyl benzoquinone present in its structure. Its therapeutic potential is bolstered by unique physical and chemical properties. Recently, Embelin, recognized as a non-peptidic, cell-permeable small inhibitor of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), has garnered significant attention for its anticancer activity. It demonstrates various anticancer mechanisms, such as apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, and autophagy, in different cancer types. Additionally, Embelin modulates several signal transduction pathways, including NF-κB, PI3Kinase/AKT, and STAT3, effectively inhibiting the proliferation of diverse cancer cell lines. This literature review illuminates the anticancer potential of Embelin, detailing its mechanisms of action and prospective clinical applications, based on relevant scientific literature from the past decade sourced from various electronic databases. See also the Graphical abstract(Fig. 1).
Keywords: Embelia ribes; Embelin; antitumor mechanisms; bioavailability; cancer; toxicity of Embelin.
Copyright © 2023 Kamath et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication, and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures





References
-
- Ahn KS, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB. Embelin, an inhibitor of X chromosome-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein, blocks the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway leading to suppression of NF-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene products. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:209–219. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.028787. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.028787. Available from: - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alam MS, Damanhouri ZA, Ahmad A, Abidin L, Amir M, Aqil M, et al. Development of response surface methodology for optimization of extraction parameters and quantitative estimation of embelin from Embelia ribes Burm by high performance liquid chromatography. Pharmacogn Mag. 2015;11(Suppl 1):S166–S172. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.157722. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.157722. Available from: - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alimbetov D, Askarova S, Umbayev B, Davis T, Kipling D. Pharmacological targeting of cell cycle, apoptotic and cell adhesion signaling pathways implicated in chemoresistance of cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1690. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061690. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061690. Available from: - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- B A, Fernandez A, Laila SP, Nair AS, Vishnu VS. Synthesis, characterization, molecular docking and anticancer studies of fluoroaniline derivatives of hydroxybenzoquinone and hydroxynaphthoquinone. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:3917–3927. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1852116. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1852116. Available from: - DOI - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
