Ameliorative inhibition of sirtuin 6 by imidazole derivative triggers oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis associated with Nrf2/Keap1 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
- PMID: 38235110
- PMCID: PMC10791838
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1335305
Ameliorative inhibition of sirtuin 6 by imidazole derivative triggers oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis associated with Nrf2/Keap1 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines
Abstract
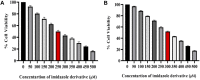
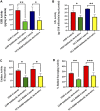
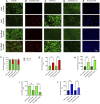
Background: Redox homeostasis is the vital regulatory system with respect to antioxidative response and detoxification. The imbalance of redox homeostasis causes oxidative stress. Nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2 (Nrf2, also called Nfe2l2)/Kelchlike ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1) signaling is the major regulator of redox homeostasis. Nrf2/Keap1 signaling is reported to be involved in cancer cell growth and survival. A high level of Nrf2 in cancers is associated with poor prognosis, resistance to therapeutics, and rapid proliferation, framing Nrf2 as an interesting target in cancer biology. Sirtuins (SIRT1-7) are class III histone deacetylases with NAD + dependent deacetylase activity that have a remarkable impact on antioxidant and redox signaling (ARS) linked with Nrf2 deacetylation thereby increasing its transcription by epigenetic modifications which has been identified as a crucial event in cancer progression under the influence of oxidative stress in various transformed cells. SIRT6 plays an important role in the cytoprotective effect of multiple diseases, including cancer. This study aimed to inhibit SIRT6 using an imidazole derivative, Ethyl 2-[5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-1-H-Imidazole-4-yl] acetate, to assess its impact on Nrf2/Keap1 signaling in A549 and NCI-H460 cell lines. Method: Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of Ethyl 2-[5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-1-H-Imidazole-4-yl] acetate was fixed by cell viability assay. The changes in the gene expression of important regulators involved in this study were examined using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and protein expression changes were confirmed by Western blotting. The changes in the antioxidant molecules are determined by biochemical assays. Further, morphological studies were performed to observe the generation of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial damage, and apoptosis. Results: We inhibited SIRT6 using Ethyl 2-[5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-1-H-Imidazole-4-yl] acetate and demonstrated that SIRT6 inhibition impacts the modulation of antioxidant and redox signaling. The level of antioxidant enzymes and percentage of reactive oxygen species scavenging activity were depleted. The morphological studies showed ROS generation, mitochondrial damage, nuclear damage, and apoptosis. The molecular examination of apoptotic factors confirmed apoptotic cell death. Further, molecular studies confirmed the changes in Nrf2 and Keap1 expression during SIRT6 inhibition. Conclusion: The overall study suggests that SIRT6 inhibition by imidazole derivative disrupts Nrf2/Keap1 signaling leading to oxidative stress and apoptosis induction.
Keywords: Epigenetics; HDAC; HDACi; KEAP1; Nrf2; SIRT6.
Copyright © 2024 Dindi, Al-Ghamdi, Alrudian, Dayel, Abuderman, Saad Alqahtani, Bahakim, Ramesh and Vilwanathan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The variable chemotherapeutic response of Malabaricone-A in leukemic and solid tumor cell lines depends on the degree of redox imbalance.Phytomedicine. 2015 Jul 15;22(7-8):713-23. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.05.007. Epub 2015 May 29. Phytomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26141757
-
SIRT6 protects retinal ganglion cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress by promoting Nrf2/ARE signaling via inhibition of Bach1.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Feb 25;300:151-158. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.01.018. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30660577
-
In-silico and in-vitro functional validation of imidazole derivatives as potential sirtuin inhibitor.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 7;10:1282820. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1282820. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38020163 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Therapeutics Targeting NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling in Cancer Oxidative Stress.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 9;13:924817. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.924817. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35754474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Nrf2 and PPARgamma in the improvement of oxidative stress in hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.Physiol Res. 2020 Dec 31;69(Suppl 4):S541-S553. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934612. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 33656904 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Expression Regulation and the Signal Transduction of Programmed Cell Death.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 16;46(9):10264-10298. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090612. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Top 100 most-cited articles on apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer over the past two decades: a bibliometrics analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 13;15:1512349. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1512349. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39872524 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

