Direct Construction of C-Alkyl Glycosides from Non-Activated Olefins via Nickel-Catalyzed C(sp3)─C(sp3) Coupling Reaction
- PMID: 38235616
- PMCID: PMC10966551
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202307226
Direct Construction of C-Alkyl Glycosides from Non-Activated Olefins via Nickel-Catalyzed C(sp3)─C(sp3) Coupling Reaction
Abstract
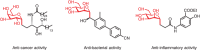
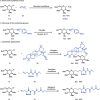
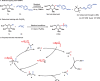
Among C-glycosides, C-alkyl glycosides are significant building blocks for natural products and glycopeptides. However, research on efficient construction methods for C-alkyl glycosides remains relatively limited. Compared with Michael acceptors, non-activated olefins are more challenging substrates and have rarely been employed in the construction of C-glycosides. Here, a highly efficient and convenient approach for the synthesis of C-alkyl glycosides through a nickel-catalyzed C(sp3)-C(sp3) coupling reaction is presented. A distinctive feature of this method is its utilization of non-activated olefins as the anomeric radical acceptors for hydroalkylation, allowing for the direct formation of C-glycoside bonds in a single step. Furthermore, this method demonstrates excellent compatibility with a broad scope of highly reactive functional groups. Mechanistic investigations suggest that the reaction proceeds via a free radical pathway, leading predominantly to the formation of products with α-configuration. Overall, this innovative methodology offers a versatile and practical approach for the synthesis of C-alkyl glycosides, offering new avenues for the production of intricate glycosides with potential applications in drug discovery and chemical biology.
Keywords: C(sp3)─C(sp3) coupling; C‐alkyl glycosides; nickel catalysis; non‐activated olefins.
© 2024 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- a) Cao X., Du X., Jiao H., An Q., Chen R., Fang P., Wang J., Yu B., Acta Pharm Sin B 2022, 12, 3783; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Jiang H., Qin X., Wang Q., Xu Q., Wang J., Wu Y., Chen W., Wang C., Zhang T., Xing D., Zhang R., Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113633; - PubMed
- c) Pan L., Cai C., Liu C., Liu D., Li G., Linhardt R. J., Yu G., Curr Opin Biotechnol 2021, 69, 191; - PubMed
- d) Valverde P., Ardá A., Reichardt N.‐C., Jiménez‐Barbero J., Gimeno A., MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1678. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Dondoni A., Marra A., Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 4395; - PubMed
- b) Yang G., Schmieg J., Tsuji M., Franck R. W., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 3818; - PubMed
- c) Franck R. W., Tsuji M., ACC. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 692; - PubMed
- d) Leclerc E., Pannecoucke X., Ethève‐Quelquejeu M., Sollogoub M., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4270. - PubMed
- e) Wei A., Boy K. M., Kishi Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9432.
-
- a) Yang Y., Yu B., Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12281; - PubMed
- b) Bennett C. S., Galan M. C., Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7931; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Ghouilem J., De Robichon M., Le Bideau F., Ferry A., Messaoudi S., Chemistry 2021, 27, 491; - PubMed
- d) Gou X.‐Y., Zhu X.‐Y., Zhang B.‐S., Liang Y.‐M., Chemistry 2023, 29, e202203351; - PubMed
- e) Shang W., Shi R., Niu D., Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 2217;
- f) Xu L.‐Y., Fan N.‐L., Hu X.‐G., Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 5095; - PubMed
- g) Azeem Z., Mandal P. K., Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 264; - PubMed
- h) Yuan Z. B., Zhu C. T., Zhang Y., Rao Y. J., Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, e202201036.
-
- a) Liu M., Niu Y., Wu Y.‐F., Ye X.‐S., Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1836; - PubMed
- b) Wang Q., An S., Deng Z., Zhu W., Huang Z., He G., Chen G., Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 793;
- c) Ding Y.‐N., Li N., Huang Y.‐C., Shi W.‐Y., Zheng N., Wang C.‐T., An Y., Liu X.‐Y., Liang Y.‐M., Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 2381; - PubMed
- d) Wang Q., Fu Y., Zhu W., An S., Zhou Q., Zhu S.‐F., He G., Liu P., Chen G., CCS. Chem. 2021, 3, 1729;
- e) Sun Q., Zhang H., Wang Q., Qiao T., He G., Chen G., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19620; - PubMed
- f) Zhu W., Sun Q., Chang H., Zhang H.‐X., Wang Q., Chen G., He G., Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 571;
- g) Ding Y.‐N., Shi W.‐Y., Liu C., Zheng N., Li M., An Y., Zhang Z., Wang C.‐T., Zhang B.‐S., Liang Y.‐M., J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 11280; - PubMed
- h) Shi W.‐Y., Ding Y.‐N., Zheng N., Gou X.‐Y., Zhang Z., Chen X., Luan Y.‐Y., Niu Z.‐J., Liang Y.‐M., Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 8945; - PubMed
- i) Gou X.‐Y., Li Y., Shi W.‐Y., Luan Y.‐Y., Ding Y.‐N., An Y., Huang Y.‐C., Zhang B.‐S., Liu X.‐Y., Liang Y.‐M., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205656; - PubMed
- j) Liu Y., Wang Y., Dai W., Huang W., Li Y., Liu H., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3491; - PubMed
- k) Yu C., Liu Y., Xie X., Hu S., Zhang S., Zeng M., Zhang D., Wang J., Liu H., Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 4926;
- l) Wu J., Kaplaneris N., Ni S., Kaltenhäuser F., Ackermann L., Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 6521; - PMC - PubMed
- m) Wu J., Wei W., Pöhlmann J., Purushothaman R., Ackermann L., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202219319; - PubMed
- n) Wu J., Kopp A., Ackermann L., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114993; - PMC - PubMed
- o) Lv W., Chen Y., Wen S., Ba D., Cheng G., J. Am. Chem. SoC. 2020, 142, 14864; - PubMed
- p) Xia L., Fan W., Yuan X.‐A., Yu S., ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 9397;
- q) Chauhan N. S., Dubey A., Mandal P. K., Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 7067; - PubMed
- r) Sakamoto K., Nagai M., Ebe Y., Yorimitsu H., Nishimura T., ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1347.
-
- a) Xia Y., Wang Y., Zhang Z., Gulzar T., Lin Y., Wang J., Zhu D., Yu B., Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 6741; - PubMed
- b) Liu J., Gong H., Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7991; - PubMed
- c) Zhao C., Jia X., Wang X., Gong H., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17645; - PubMed
- d) Wang Q., Sun Q., Jiang Y., Zhang H., Yu L., Tian C., Chen G., Koh M. J., Nat Synth 2022, 1, 235;
- e) Shang W., Niu D., ACC. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 2473; - PubMed
- f) Xu S., Zhang W., Li C., Li Y., Zeng H., Wang Y., Zhang Y., Niu D., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202218303; - PubMed
- g) Zhang C., Xu S. Y., Zuo H., Zhang X., Dang Q. D., Niu D. W., Nat Synth 2023, 2, 251;
- h) Xie D., Wang Y., Zhang X., Fu Z., Niu D., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202204922; - PubMed
- i) Mou Z.‐D., Wang J.‐X., Zhang X., Niu D., Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 3025;
- j) Jiang Y., Zhang Y., Lee B. C., Koh M. J., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202305138; - PubMed
- k) Wang Q., Lee B. C., Song N., Koh M. J., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301081; - PubMed
- l) Jiang Y., Yang K., Wei Y., Wang Q., Li S.‐J., Lan Y., Koh M. J., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211043; - PubMed
- m) Wang Q., Lee B. C., Tan T. J., Jiang Y., Ser W. H., Koh M. J., Nat Synth 2022, 1, 967;
- n) Chen A., Zhao S., Han Y., Zhou Z., Yang B., Xie L.‐G., Walczak M. A., Zhu F., Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7569. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2022YFA1302900/National Key R&D Program of China
- H.L/National Key R&D Program of China
- 82130105/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22337003/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82121005/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- H.L/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22177124/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82322063/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- J.W/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 22107107/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- W.H.D/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LG-GG-202204-02/Lingang Laboratory
- J.W/Lingang Laboratory
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources