pUdOs: Concise Plasmids for Bacterial and Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 38235654
- PMCID: PMC10878396
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00408
pUdOs: Concise Plasmids for Bacterial and Mammalian Cells
Abstract
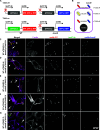
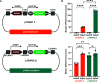
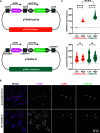
The plasmids from the Université d'Ottawa (pUdOs) are 28 small plasmids each comprising one of four origins of replication and one of seven selection markers, which together afford flexible use in Escherichia coli and several related gram-negative bacteria. The promoterless multicloning site is insulated from upstream spurious promoters by strong transcription terminators and contains type IIP or IIS restriction sites for conventional or Golden Gate cloning. pUdOs can be converted into efficient expression vectors through the insertion of a promoter at the user's discretion. For example, we demonstrate the utility of pUdOs as the backbone for an improved version of a Type III Secretion System reporter in Shigella. In addition, we derive a series of pUdO-based mammalian expression vectors, affording distinct levels of expression and transfection efficiency comparable to commonly used mammalian expression plasmids. Thus, pUdOs could advantageously replace traditional plasmids in a wide variety of cell types and applications.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Shigella; mammalian cell expression; plasmid; proteobacteria; type III secretion system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Thomas C. M.; Summers D.. Bacterial Plasmids. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; 2008.
-
- Chan V.; Dreolini L.; Flintoff K. A.; Lloyd S. J.; Mattenley A. A.. The Effect of Increasing Plasmid Size on Transformation Efficiency in Escherichia coli. In Proceedings of the Journal of Experimental Microbiology and Immunology; UBC, Department of Microbiology and Immunology; 2002; vol 2, pp 207–223.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

