An optimized relational database for querying structural patterns in proteins
- PMID: 38236197
- PMCID: PMC10939390
- DOI: 10.1093/database/baad093
An optimized relational database for querying structural patterns in proteins
Abstract
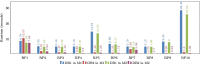
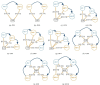
A database is an essential component in almost any software system, and its creation involves more than just data modeling and schema design. It also includes query optimization and tuning. This paper focuses on a web system called GSP4PDB, which is used for searching structural patterns in proteins. The system utilizes a normalized relational database, which has proven to be inefficient even for simple queries. This article discusses the optimization of the GSP4PDB database by implementing two techniques: denormalization and indexing. The empirical evaluation described in the article shows that combining these techniques enhances the efficiency of the database when querying both real and artificial graph-based structural patterns.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
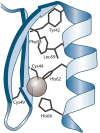
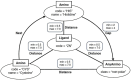




References
-
- Dhifli Abdoulaye W. (2015) PGR: a novel graph repository of protein 3D-structures. J. Data Mining in Genomics & Proteomics, 6, 1–4.
-
- Anders G. and Nicola M. (2011). Managing the Protein Data Bank with DB2 pureXML IBM developerWorks, Technical Library.
-
- Angles R. and Arenas M. (2018) A graph-based approach for querying protein-ligand structural patterns. In: Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics, 10813, Springer, Cham, pp. 235–244.
-
- Aslam N., Nadeem A. and Ellahi Babar M. et al. (2016) RPDB: A relational databank of protein structures. Pak. J. Agric. Sci., 53, 129–134.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

