Design and Synthesis of Dual-Targeting Inhibitors of sEH and HDAC6 for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mortality
- PMID: 38236416
- PMCID: PMC11308793
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02006
Design and Synthesis of Dual-Targeting Inhibitors of sEH and HDAC6 for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mortality
Abstract
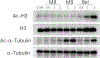
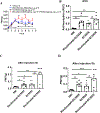
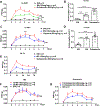
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids with anti-inflammatory effects are inactivated by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). Both sEH and histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) inhibitors are being developed as neuropathic pain relieving agents. Based on the structural similarity, we designed a new group of compounds with inhibition of both HDAC6 and sEH and obtained compound M9. M9 exhibits selective inhibition of HDAC6 over class I HDACs in cells. M9 shows good microsomal stability, moderate plasma protein binding rate, and oral bioavailability. M9 exhibited a strong analgesic effect in vivo, and its analgesic tolerance was better than gabapentin. M9 improved the survival time of mice treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and reversed the levels of inflammatory factors induced by LPS in mouse plasma. M9 represents the first sEH/HDAC6 dual inhibitors with in vivo antineuropathic pain and anti-inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest conflict.
Figures
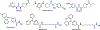





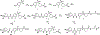


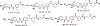
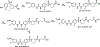



References
-
- Treede RD; Jensen TS; Campbell JN; Cruccu G; Dostrovsky JO; Griffin JW; Hansson P; Hughes R; Nurmikko T; Serra J Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008, 70, 1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Bannister K; Sachau J; Baron R; Dickenson AH Neuropathic pain: mechanism-based therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 257–274. - PubMed
-
- Finnerup NB; Kuner R; Jensen TS Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. - PubMed
-
- Bair MJ; Robinson RL; Katon W; Kroenke K Depression and pain comorbidity: a literature review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 2433–2445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

