Downregulation of the kidney glucagon receptor, essential for renal function and systemic homeostasis, contributes to chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 38237602
- PMCID: PMC10932880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.12.024
Downregulation of the kidney glucagon receptor, essential for renal function and systemic homeostasis, contributes to chronic kidney disease
Abstract
The glucagon receptor (GCGR) in the kidney is expressed in nephron tubules. In humans and animal models with chronic kidney disease, renal GCGR expression is reduced. However, the role of kidney GCGR in normal renal function and in disease development has not been addressed. Here, we examined its role by analyzing mice with constitutive or conditional kidney-specific loss of the Gcgr. Adult renal Gcgr knockout mice exhibit metabolic dysregulation and a functional impairment of the kidneys. These mice exhibit hyperaminoacidemia associated with reduced kidney glucose output, oxidative stress, enhanced inflammasome activity, and excess lipid accumulation in the kidney. Upon a lipid challenge, they display maladaptive responses with acute hypertriglyceridemia and chronic proinflammatory and profibrotic activation. In aged mice, kidney Gcgr ablation elicits widespread renal deposition of collagen and fibronectin, indicative of fibrosis. Taken together, our findings demonstrate an essential role of the renal GCGR in normal kidney metabolic and homeostatic functions. Importantly, mice deficient for kidney Gcgr recapitulate some of the key pathophysiological features of chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; glucagon receptor; kidney.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

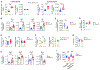



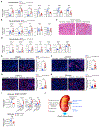
Comment in
-
The renal glucagon receptor is essential to kidney metabolic and homeostatic functions.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 Apr;20(4):203. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00825-1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38424242 No abstract available.
References
-
- Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, and Masson P (2017). Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 389, 1238–1252. - PubMed
-
- Gansevoort RT, Correa-Rotter R, Hemmelgarn BR, Jafar TH, Heerspink HJL, Mann JF, Matsushita K, and Wen CP (2013). Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 382, 339–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

