Identification of a Novel Subtype-Selective α1B-Adrenoceptor Antagonist
- PMID: 38238043
- PMCID: PMC10854767
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00767
Identification of a Novel Subtype-Selective α1B-Adrenoceptor Antagonist
Abstract
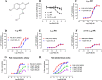
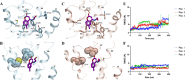
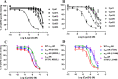
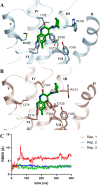
α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenoceptors (α1-ARs) are members of the adrenoceptor G protein-coupled receptor family that are activated by adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline. α1-ARs are clinically targeted using antagonists that have minimal subtype selectivity, such as prazosin and tamsulosin, to treat hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia, respectively. Abundant expression of α1-ARs in the heart and central nervous system (CNS) makes these receptors potential targets for the treatment of cardiovascular and CNS disorders, such as heart failure, epilepsy, and Alzheimer's disease. Our understanding of the precise physiological roles of α1-ARs, however, and their involvement in disease has been hindered by the lack of sufficiently subtype-selective tool compounds, especially for α1B-AR. Here, we report the discovery of 4-[(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-6-methyl-2H-chromen-2-one (Cpd1), as an α1B-AR antagonist that has 10-15-fold selectivity over α1A-AR and α1D-AR. Through computational and site-directed mutagenesis studies, we have identified the binding site of Cpd1 in α1B-AR and propose the molecular basis of α1B-AR selectivity, where the nonconserved V19745.52 residue plays a major role, with contributions from L3146.55 within the α1B-AR pocket. By exploring the structure-activity relationships of Cpd1 at α1B-AR, we have also identified 3-[(cyclohexylamino)methyl]-6-methylquinolin-2(1H)-one (Cpd24), which has a stronger binding affinity than Cpd1, albeit with reduced selectivity for α1B-AR. Cpd1 and Cpd24 represent potential leads for α1B-AR-selective drug discovery and novel tool molecules to further study the physiology of α1-ARs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

