Equity of health resource allocation in Chongqing, China, in 2021: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38238051
- PMCID: PMC10806633
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078987
Equity of health resource allocation in Chongqing, China, in 2021: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Chongqing, the most populous city in Southwest China. This study aims to examine the equity of health resource allocation in Chongqing using the latest statistics, analyse possible shortcomings and propose strategies to address these issues.
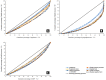
Methods: This cross-sectional study used healthcare resource, population, area and gross domestic product data from the Seventh National Census Bulletin of Chongqing, the National County Statistical Yearbook, the Chongqing Municipal Bureau of Statistics and the Chongqing Health Statistical Yearbook 2022. We also studied the equity of health resource allocation in Chongqing by using the Gini coefficient, Lorenz curve and Theil index, and used the Analytical Hierarchy Process and Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (AHP-TOPSIS) method to comprehensively evaluate the health resources in the four major regions of Chongqing.
Results: The Gini coefficient of health resources in Chongqing in 2021 was the highest when allocated according to geographical area, between 0.4285 and 0.6081, both of which exceeded 0.4, and the Gini coefficient of medical equipment was the highest and exceeded 0.6. The inter-regional Theil index of each resource was greater than the intraregional Theil index, and the contribution of inter-regional differences ranged from 64.83% to 80.21%. The results of the AHP-TOPSIS method showed that the relative proximity between health resources and ideal solutions in four regions of Chongqing ranged from 0.0753 to 0.9277.
Conclusion: The allocation of health resources in Chongqing exhibits pronounced inequities, particularly in the distribution of medical equipment according to geographical area. Moreover, there exists a substantial gap in the equity of health resource allocation among the four regions of Chongqing. As such, this study emphasises the need for Chongqing, China, to prioritise the equitable allocation of health resources and increase consideration of geographic factors. Implementing measures to promote equitable allocation of health resources, particularly in geographic terms, is critical.
Keywords: HEALTH ECONOMICS; HEALTH SERVICES ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT; Health Equity; Health policy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Geographic variations, temporal trends, and equity in healthcare resource allocation in China, 2010-21.J Glob Health. 2025 Jan 17;15:04008. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04008. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 39819771 Free PMC article.
-
National equity of health resource allocation in China: data from 2009 to 2013.Int J Equity Health. 2016 Apr 19;15:68. doi: 10.1186/s12939-016-0357-1. Int J Equity Health. 2016. PMID: 27093960 Free PMC article.
-
Equity and efficiency of public hospitals' health resource allocation in Guangdong Province, China.Int J Equity Health. 2022 Sep 22;21(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12939-022-01741-1. Int J Equity Health. 2022. PMID: 36138478 Free PMC article.
-
Fairness of the Distribution of Public Medical and Health Resources.Front Public Health. 2021 Nov 10;9:768728. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.768728. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34858935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Equality of Medical Health Resource Allocation in China Based on the Gini Coefficient Method.Iran J Public Health. 2015 Apr;44(4):445-57. Iran J Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26056663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Equity in the geographical distribution of general practitioners in Iran.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024 Sep 24;4(9):e0003609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0003609. eCollection 2024. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39316616 Free PMC article.
-
A study on regional differences and convergence of nursing human resource levels in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: an empirical study.BMC Nurs. 2024 Oct 24;23(1):781. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-02446-2. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39449148 Free PMC article.
-
Equity and efficiency of public health resource allocation in China.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 23;25(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21447-7. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39849405 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial-temporal evolution of the allometric relationship between urban economic and health resources in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0314315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314315. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854516 Free PMC article.
-
A three-tier AI solution for equitable glaucoma diagnosis across China's hierarchical healthcare system.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 Jul 3;8(1):400. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01835-4. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 40610592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu F, Chen W, Lin L, et al. . The balanced allocation of medical and health resources in urban areas of China from the perspective of sustainable development: a case study of Nanjing. Sustainability 2022;14:6707. 10.3390/su14116707 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous