Synthesis of the I-K Fused Polyether Array of CTX3C and Related Ciguatoxins by Use of a Gold-Catalyzed Cyclization Reaction
- PMID: 38238251
- PMCID: PMC10845158
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.3c03782
Synthesis of the I-K Fused Polyether Array of CTX3C and Related Ciguatoxins by Use of a Gold-Catalyzed Cyclization Reaction
Abstract
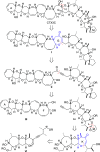
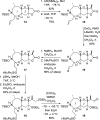
The I-K fragment (C31-C49) of the ciguatoxin CTX3C has been synthesized from a simple chiral pool derived tetrahydropyranyl alcohol. An efficient gold-catalyzed cyclization reaction of a γ'-hydroxy ynone has been used to accomplish efficient closure of ring K under mild conditions. The resulting vinylogous ester has been elaborated to give a complete tricyclic fragment bearing the dimethyl-substituted side chain required for assembly of the LM spirocyclic acetal portion of the target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolution of a practical total synthesis of ciguatoxin CTX3C.Acc Chem Res. 2004 Dec;37(12):961-8. doi: 10.1021/ar0301577. Acc Chem Res. 2004. PMID: 15609988
-
Stereoselective 6-exo radical cyclization using cis-vinyl sulfoxide: practical total synthesis of CTX3C.J Nat Prod. 2011 Mar 25;74(3):357-64. doi: 10.1021/np100729d. Epub 2011 Jan 20. J Nat Prod. 2011. PMID: 21250701
-
Two convergent routes to the left-wing fragment of ciguatoxin CTX3C using O,S-acetals as key intermediates.Org Lett. 2006 Dec 7;8(25):5805-8. doi: 10.1021/ol062350h. Org Lett. 2006. PMID: 17134277
-
Construction of fused polycyclic ethers by strategies involving ring-closing metathesis.Chem Commun (Camb). 2006 Sep 14;(34):3571-81. doi: 10.1039/b601839d. Epub 2006 May 30. Chem Commun (Camb). 2006. PMID: 17047770 Review.
-
Convergent syntheses of polycyclic ethers. Illustrations of the utility of acetal-linked intermediates.Org Biomol Chem. 2004 Jul 7;2(13):1811-7. doi: 10.1039/b407187e. Epub 2004 Jun 14. Org Biomol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15227529 Review.
References
-
- Satake M.; Murata M.; Yasumoto T. The Structure of CTX3C, a Ciguatoxin Congener Isolated from Cultured Gambierdiscus Toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1975–1978. 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)91978-6. - DOI
-
- Frelin C.; Durand-Clément M.; Bidard J.-N.; Lazdunski M.. The Molecular Basis of Ciguatoxin Action. In Marine Toxins; Hall S., Strichartz G., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Vol. 418, Chapter 13, pp 192–199.
-
- Friedman M. A.; Fernandez M.; Backer L. C.; Dickey R. W.; Bernstein J.; Schrank K.; Kibler S.; Stephan W.; Gribble M. O.; Bienfang P.; Bowen R. E.; Degrasse S.; Flores Quintana H. A.; Loeffler C. R.; Weisman R.; Blythe D.; Berdalet E.; Ayyar R.; Clarkson-Townsend D.; Swajian K.; Benner R.; Brewer T.; Fleming L. E. An Updated Review of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: Clinical, Epidemiological, Environmental, and Public Health Management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72.10.3390/md15030072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

