Peptidyl nitroalkene inhibitors of main protease rationalized by computational and crystallographic investigations as antivirals against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 38238420
- PMCID: PMC10796436
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-024-01104-7
Peptidyl nitroalkene inhibitors of main protease rationalized by computational and crystallographic investigations as antivirals against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
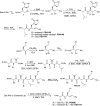
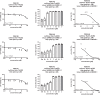
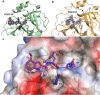
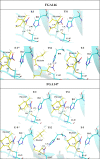
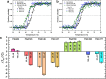
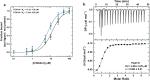
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to represent a global public health issue. The viral main protease (Mpro) represents one of the most attractive targets for the development of antiviral drugs. Herein we report peptidyl nitroalkenes exhibiting enzyme inhibitory activity against Mpro (Ki: 1-10 μM) good anti-SARS-CoV-2 infection activity in the low micromolar range (EC50: 1-12 μM) without significant toxicity. Additional kinetic studies of compounds FGA145, FGA146 and FGA147 show that all three compounds inhibit cathepsin L, denoting a possible multitarget effect of these compounds in the antiviral activity. Structural analysis shows the binding mode of FGA146 and FGA147 to the active site of the protein. Furthermore, our results illustrate that peptidyl nitroalkenes are effective covalent reversible inhibitors of the Mpro and cathepsin L, and that inhibitors FGA145, FGA146 and FGA147 prevent infection against SARS-CoV-2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
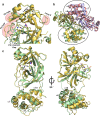
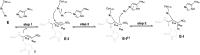
Similar articles
-
Discovery of quinazolin-4-one-based non-covalent inhibitors targeting the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 main protease (SARS-CoV-2 Mpro).Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Sep 5;257:115487. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115487. Epub 2023 May 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37257212 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Crystallographic Studies of Nonpeptidic Piperazine Derivatives as Covalent SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2022 Dec 22;65(24):16902-16917. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01716. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36475694
-
Covalent and non-covalent binding free energy calculations for peptidomimetic inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021 Mar 21;23(11):6746-6757. doi: 10.1039/d1cp00266j. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 33711090
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Dimerization of the Main Protease of Coronaviruses: A Potential Broad-Spectrum Therapeutic Strategy.ACS Comb Sci. 2020 Jun 8;22(6):297-305. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.0c00058. Epub 2020 May 27. ACS Comb Sci. 2020. PMID: 32402186 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring covalent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: from peptidomimetics to novel scaffolds.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025 Dec;40(1):2460045. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2025.2460045. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39912405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Reflection on the Use of Molecular Simulation to Respond to SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Threats.J Phys Chem Lett. 2025 Apr 3;16(13):3249-3263. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c03654. Epub 2025 Mar 21. J Phys Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40118074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-1919 - 21 December 2022. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-weekly-epidemiological-....
-
- Editorial “There’s no room for COVID complacency in 2023”. Nature613, 7 (2023). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- PIE-202020E224/Fundación General CSIC (Fundación General Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas)
- IDIFEDER/2021/02/Generalitat Valenciana (Regional Government of Valencia)
- SEJI/2020/007/Generalitat Valenciana (Regional Government of Valencia)
- UJI-B2020-03/Universitat Jaume I (Universitat Jaume I de Castelló)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

