Self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator sensor for detecting humidity level and monitoring ethanol variation in a simulated exhalation environment
- PMID: 38238422
- PMCID: PMC10796746
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-51862-6
Self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator sensor for detecting humidity level and monitoring ethanol variation in a simulated exhalation environment
Abstract
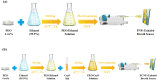
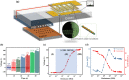
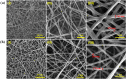
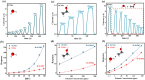
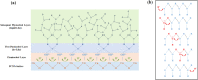
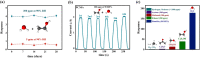
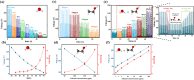
Respiration stands as a vital process reflecting physiological and pathological human health status. Exhaled breath analysis offers a facile, non-invasive, swift, and cost-effective approach for diagnosing and monitoring diseases by detecting concentration changes of specific biomarkers. In this study, we employed Polyethylene oxide/copper (I) oxide composite nanofibers (PCNFs), synthesized via the electrospinning method as the sensing material to measure ethanol levels (1-200 ppm) in an exhaled breath simulator environment. The integrated contact-separation triboelectric nanogenerator was utilized to power the self-powered PCNFs exhaled breath sensor. The PCNFs-based gas sensor demonstrates promising results with values of 0.9 and 3.2 for detecting 5 ppm and 200 ppm ethanol, respectively, in the presence of interfering gas at 90% relative humidity (RH). Notably, the sensor displayed remarkable ethanol selectivity, with ratios of 10:1 to methanol and 25:1 to acetone. Response and recovery times for 200 ppm ethanol at 90 RH% were rapid, at 2.7 s and 5.8 s, respectively. The PCNFs-based exhaled breath sensor demonstrated consistent and stable performance in practical conditions, showcasing its potential for integration into wearable devices. This self-powered breath sensor enabling continuous monitoring of lung cancer symptoms and facilitating compliance checks with legal alcohol consumption limits.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Yu, S., Zhang, H. & Zhang, J. Highly sensitive self-powered RGO-TiO2 humidity sensor driven by triboelectric nanogenerator for human respiratory monitoring. https://ssrn.com/abstract=3993237.
-
- Shen S, Xiao X, Xiao X, Chen J. Triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered breath monitoring. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022;5:3952–3965. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.1c02465. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

