Cell cycle specific, differentially tagged ribosomal proteins to measure phase specific transcriptomes from asynchronously cycling cells
- PMID: 38238470
- PMCID: PMC10796924
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-52085-5
Cell cycle specific, differentially tagged ribosomal proteins to measure phase specific transcriptomes from asynchronously cycling cells
Abstract
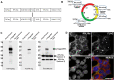
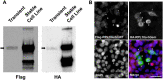
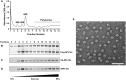
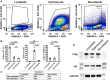
Asynchronously cycling cells pose a challenge to the accurate characterization of phase-specific gene expression. Current strategies, including RNAseq, survey the steady state gene expression across the cell cycle and are inherently limited by their inability to resolve dynamic gene regulatory networks. Single cell RNAseq (scRNAseq) can identify different cell cycle transcriptomes if enough cycling cells are present, however some cells are not amenable to scRNAseq. Therefore, we merged two powerful strategies, the CDT1 and GMNN degrons used in Fluorescent Ubiquitination-based Cell Cycle Indicator (FUCCI) cell cycle sensors and the ribosomal protein epitope tagging used in RiboTrap/Tag technologies to isolate cell cycle phase-specific mRNA for sequencing. The resulting cell cycle dependent, tagged ribosomal proteins (ccTaggedRP) were differentially expressed during the cell cycle, had similar subcellular locations as endogenous ribosomal proteins, incorporated into ribosomes and polysomes, and facilitated the recovery of cell cycle phase-specific RNA for sequencing. ccTaggedRP has broad applications to investigate phase-specific gene expression in complex cell populations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combinatorial action of transcription factors orchestrates cell cycle-dependent expression of the ribosomal protein genes and ribosome biogenesis.FEBS J. 2014 May;281(10):2339-52. doi: 10.1111/febs.12786. Epub 2014 Apr 7. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24646001
-
Identification and characterization of distinct cell cycle stages in cardiomyocytes using the FUCCI transgenic system.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Nov 15;408(2):112880. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112880. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34655601
-
In vivo labelling of functional ribosomes reveals spatial regulation during starvation in Podospora anserina.BMC Genet. 2000;1:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-1-3. Epub 2000 Nov 16. BMC Genet. 2000. PMID: 11112985 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal heterogeneity - A new inroad for pharmacological innovation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 May;175:113874. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113874. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32105657 Review.
-
The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast.Trends Biochem Sci. 1999 Nov;24(11):437-40. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01460-7. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999. PMID: 10542411 Review.
Cited by
-
Ribosome specialization in cancer: a spotlight on ribosomal proteins.NAR Cancer. 2024 Jul 9;6(3):zcae029. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae029. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38989007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poor statistical reporting, inadequate data presentation and spin persist despite Journal awareness and updated Information for Authors.F1000Res. 2023 Nov 20;12:1483. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.142841.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 38434651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barres BA, Silverstein BE, Corey DP, Chun LL. Immunological, morphological, and electrophysiological variation among retinal ganglion cells purified by panning. Neuron. 1988;1(9):791–803. - PubMed
-
- Cleary MD, Meiering CD, Jan E, Guymon R, Boothroyd JC. Biosynthetic labeling of RNA with uracil phosphoribosyltransferase allows cell-specific microarray analysis of mRNA synthesis and decay. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23(2):232–237. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

